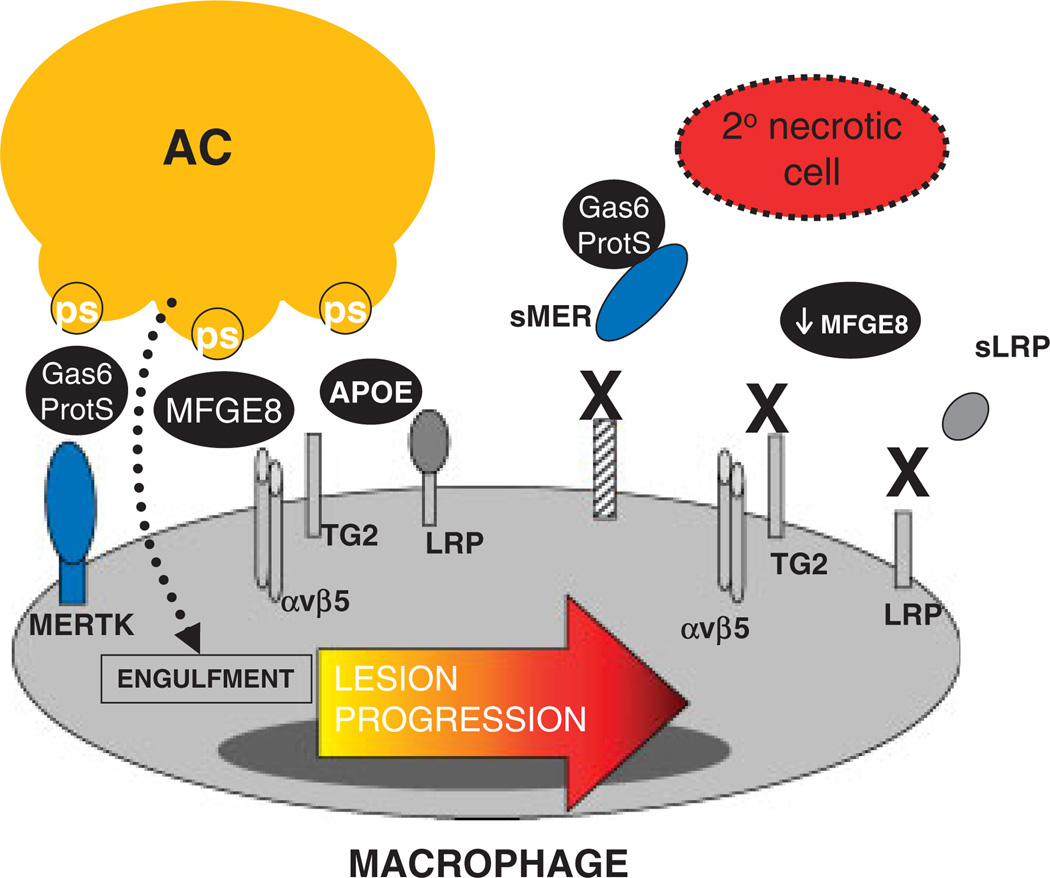
Figure 1.
Possible mechanisms of defective efferocytosis by macrophages in advanced atherosclerosis. Depicted here are several molecules that have been shown to a play a role in macrophage efferocytosis in atherosclerosis. These include the efferocytosis receptors MERTK, αvβ5 integrin, TG2, and LRP (low density lipoprotein related protein). AC receptors can engage bridging molecules such as Gas6/Protein S or MFGE8, which facilitate binding to and phosphatidylserine (PS). There are several hypotheses as to why efferocytosis loses efficiency in advanced plaques, including dysfunction of the molecules as a result of cleavage (MERTK and LRP leading to the soluble isoforms sMER and sLRP respectively), decreased expression (MFGE8), or competitive inhibition by other plaque molecules (sLRP).