Fig. 6.
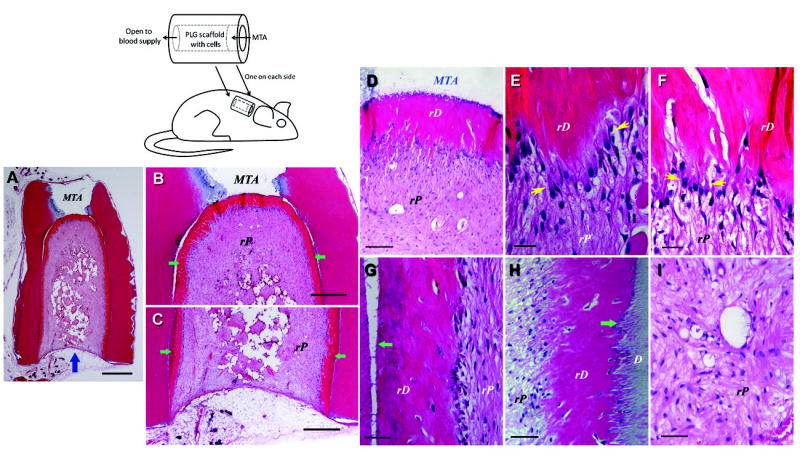
De novo regeneration of human dental pulp/dentin. Illustration at upper left depicts SCID mouse subcutaneous study model for pulp/dentin regeneration. The canal space of human tooth root fragments (~6–7 mm long) was enlarged to ~2.5 mm in diameter. One end of the canal opening was sealed with MTA cement. (A–I) Histological analysis of in vivo pulp/dentin regeneration using SCAP. A root fragment was prepared and the canal space inserted with SCAP/PLG and transplanted into a SCID mouse for 3 months. The sample was harvested and processed for H&E staining. D, original dentin; rD, regenerated dentin-like tissue; rP, regenerated pulp-like tissue. Blue arrow in (A) indicates the blood supply entrance; green arrows in (B&C) indicate continuous layer of uniformed thickness of rD; yellow arrows in (E&F) indicate the region of well-aligned odontoblast-like cells with polarized cell bodies; green arrows in (G&H) indicate junctions between D and rD. Scale bars: (A) 1 mm; (B& C) 500 μm. (D) 100 μm; (E & F) 20 μm; (G–I) 50 μm. (Adapted from (85) with permission)
