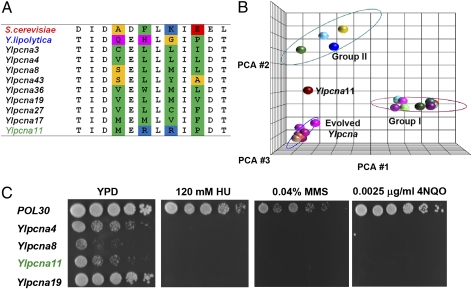
Fig. 6.
In vitro evolution of Y. lipolytica PCNA for complementation of ScPCNA in S. cerevisiae. (A) Sequence alignment of 9 unique mutants identified following selection for viability. The mutated positions are mostly hydrophobic and are highlighted in color (using the color scheme described in the legend for Fig. 2). (B) PCA analysis of the 9 unique sequences of the evolved clones, together with the 23 natural IDCL sequences (described in Fig. 2). The analysis indicates that the evolved Ylpcna mutants fall into a unique group that is different from the two natural groups, except for YlPCNA11, which is significantly different in its sequence. (C) HU, MMS, and 4-nitroquinoline-N-oxide (4NQO) sensitivity of the evolved Ylpcna mutants.