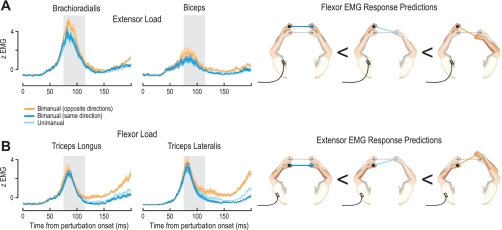
Fig. 4.
Rapid responses in the perturbed arm are modulated by contralateral perturbations: EMG traces from the perturbed limb in the coupled single-object task when the contralateral arm is unperturbed (light blue) or perturbed in the same (dark blue) or opposite (orange) direction. Schematics on right of the plots show EMG recorded from the left arm under the 3 possible perturbation conditions of the contralateral arm, with the initial bar orientation prior to perturbation represented by the gray dotted line. EMG averages shown in the plots also include the mirror-symmetric conditions for EMG recorded from the perturbed right arm under the 3 perturbation states of the left arm. A: traces represent averaged EMG (normalized) across all subjects during extension perturbations of the recorded arm in the extensor background load condition, as a function of whether the contralateral arm was unperturbed (clamped, light blue trace) or perturbed in the same (dark blue trace) or opposite (orange trace) directions. B: extensor EMG responses during flexion perturbations of the recorded arm in the flexor background load condition under 3 perturbation states of the contralateral arm. Shaded areas in trace plots signify ±SE, and the gray shaded areas behind the traces indicate the 40-ms period used for statistical analyses (75–115 ms).