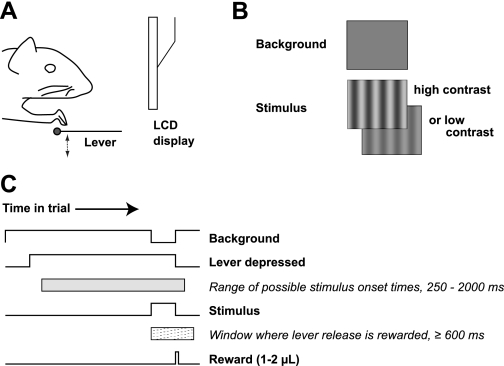
Fig. 1.
Behavioral task. Mice perform a visual change detection task by manipulating a lever while their heads are held fixed. A: schematic; animals sit on all fours in front of a liquid crystal display (LCD) where visual stimuli are presented; the lever is positioned below 1 forepaw. Approximately 20 mN (∼2 gram-force) are required to depress the lever. B: visual stimuli are vertically oriented sinusoidal gratings of varying contrast and spatial frequency. The background is a spatially constant gray. C: time course of a single trial. Animals initiate the trial by depressing the lever; the stimulus is displayed at a random time, and animals must report detecting the stimulus by releasing the lever. Correct responses within a reaction time window of 600 or 700 ms (no difference in behavior was observed; see methods) after stimulus onset are rewarded with a water drop.