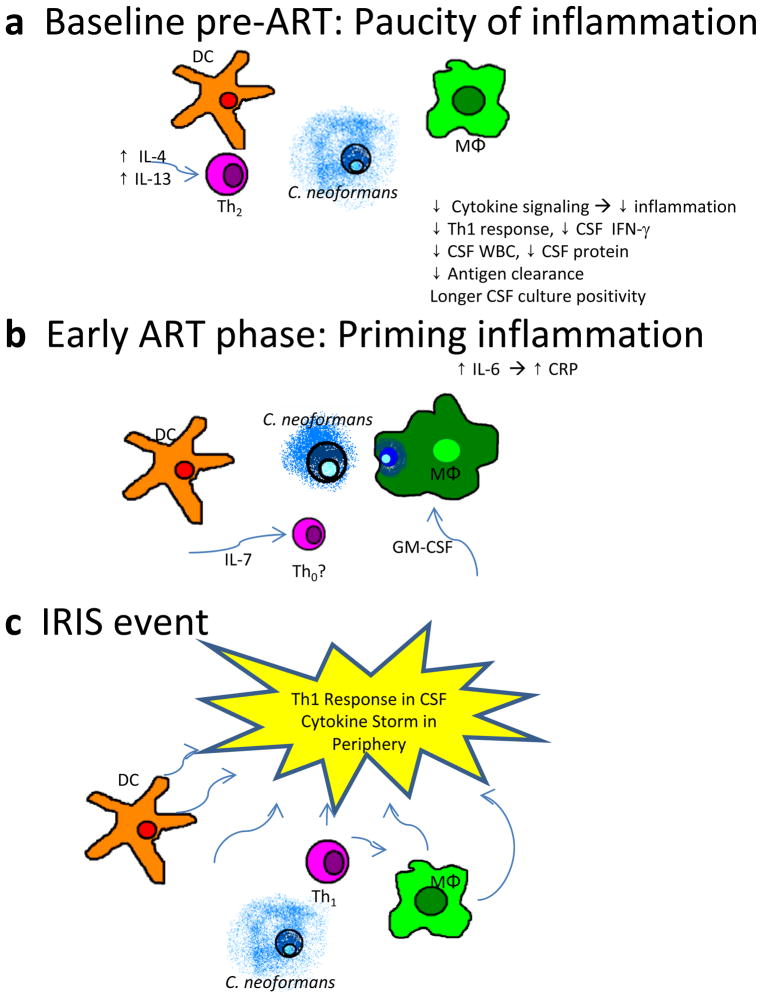
Figure 2.
Pathogenesis of cryptococcal immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS), which has three phases: a Before antiretroviral therapy (ART), inappropriate signals lead to a nonprotective type-2 helper T-cell (Th2) response and failure to clear the antigen. b During initial ART immune recovery, pro-inflammatory signaling by antigen-presenting cells does not produce an effector response. c During an IRIS event, a cytokine storm occurs in the periphery and a predominant type-1 helper T-cell (Th1) effector response is evident in the central nervous system, with both sites experiencing increased inflammation and possible absence of regulatory mechanisms. CSF cerebrospinal fluid; DC dendritic cells; GM-CSF granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IFN interferon; IL interleukin; MΦ macrophage; WBC white blood cells.