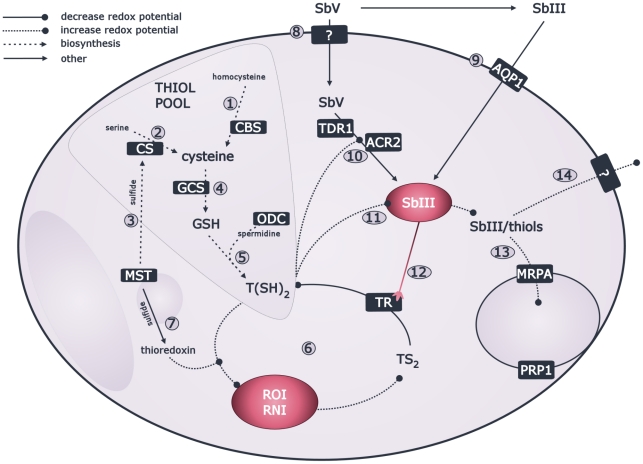
Figure 1. Overview of Leishmania pathways involved in response to SSG.
The defence against oxidative and nitrosative radicals imposed by macrophages relies on antioxidants here represented in the thiol pool with 3 major thiols: (a) cysteine with 2 synthesis pathways in trypanosomatids including transsulfuration pathway (as in vertebrates) via homocysteine with a key enzyme cystathione β-synthase (CBS) (#1), and de novo synthesis from serine (as in some prokaryotes and eukaryotes) catalysed by cysteine synthase (CS) (#2); with sulfide possibly provided by mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase (MST) (#3) [60], [61]; (b) glutathione (GSH) synthesised by condensation of cysteine and glutamate with the key enzyme γ-glutamylcysteine synthase (GCS) (#4) [62]; and (c) trypanothione (T(SH)2) which is synthesised by condensation of glutathione and spermidine; with ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) as key enzyme of spermidine synthesis (#5) [63]. Maintenance of redox balance is centred around the strong reductant T(SH)2 and the flavo-enzyme trypanothione reductase (TR) which keeps the T(SH)2 pool reduced and the redox potential low (#6) [40], [63]–[65]; MST possibly also has an antioxidant role via thioredoxin (#7) [61]. The drug SbV can be taken up by the parasite via an unidentified transporter (#8) [66] and the reduced form SbIII gains access via aquaglyceroporin (AQP1) (#9) [67]. The reduction of SbV to SbIII involves thiols and can be a non-enzymatical spontaneous reduction [68]–[71], or enzymatically catalyzed by thiol dependent reductase 1 (TDR1) [72] or arsenate reductase 2 (ACR2) [73] (#10). The resulting SbIII can form conjugates with thiols and inhibit TR (#12), together leading to increase of redox potential [12]–[14], [39]. The SbIII/thiol conjugates can be sequestered by ABC transporter multidrug resistance protein A (MRPA) or possibly pentamidine resistance protein 1 (PRP1) [74], [75] into intracellular organelles (#13), or can be directly pumped out by an uncharacterised transporter (#14) [76] (boxed names = proteins of which the corresponding genes were chosen for DNA sequencing and gene expression profiling in this study, unboxed names = metabolites; used abbreviations: ROI = reactive oxygen intermediates, RNI = reactive nitrogen intermediates).