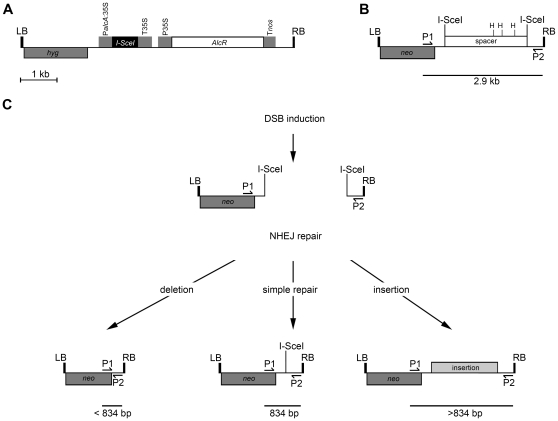
Figure 1. Overview of EtOH induced induction of DSBs.
The T-DNA of vector pAlcR:ISceI (A) contains the left (LB) and right border (RB) sequences; a hygromycin selectable marker gene (hyg); the AlcR gene constitutively expressed from the 35S promoter; and the I-SceI gene driven by the alcA:35S promoter. In the presence of EtOH, AlcR binds to and transcriptionally activates the alcA:35S promoter, driving expression of I-SceI. The T-DNA of vector pdao1 (B) contains left and right border sequences; a kanamycin selectable marker gene (neo); and a spacer region flanked by I-SceI target sites. The spacer region also contains three HincII sites (H). (C) Upon I-SceI expression the I-SceI sites are cleaved leading to the excision of the spacer region. DSB repair will then result in the joining of the cleaved sequences. This may result in direct joining of the I-SceI restriction sites, deletion of sequence on either side of the DSB or insertion of sequence at the site of DSB repair. These three types of repair can be distinguished by PCR using primers P1 (DSBF1) and P2 (DSBR1) that flank the site of DSB repair. Direct joining will result in an 834 bp product whilst deletion will result in a smaller product and insertion in a larger product. In the absence of DSB induction or when DSBs are repaired by HR the spacer region will not be excised resulting in a PCR product of 2.9 kb (B). Amplification of this product will be prevented by digesting template DNA with HincII.