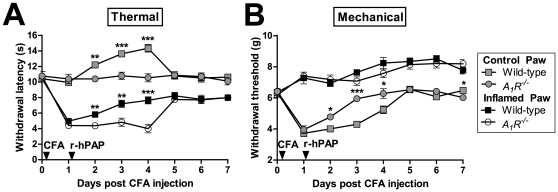
Figure 7. Antinociceptive effects of r-hPAP in chronic inflammatory pain model.
(A, B) CFA was injected into one hindpaw (CFA-arrow) of wild-type (n = 10) and A1R−/− mice (n = 10). r-hPAP (250 mU) was intrathecally injected 1 day later (r-hPAP-arrow). Inflamed and non-inflamed (control) hindpaws were tested for (A) thermal and (B) mechanical sensitivity. Data are plotted as means ± SEM. Paired t-tests were used to compare responses at each time point between genotypes, same paw comparisons. *p<0.05, **p<0.005, ***p<0.0005.