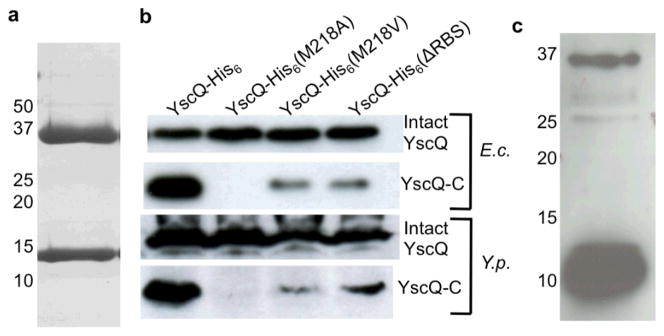
Figure 1.
YscQ-C results from an internal translation initiation site. (a) YscQ expressed in E. coli and purified by Ni2+-chelation and size-exclusion chromatography, as visualized by Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE. Molecular mass markers are indicated at left. Intact YscQ is the upper band at ~36 kDa and YscQ-C the lower band at ~11 kDa. (b) Wild-type and mutant YscQ expressed in E. coli (top two blots) and Y. pseudotuberculosis (bottom two), and detected by anti-His western blot from whole cell lysates. YscQ contains a C-terminal His-tag, and was detected as intact YscQ (upper panel in each set) and YscQ-C (lower panel in each set). (c) YscQ detected in Y. pseudotuberculosis by Western blot using anti-YscQ polyclonal antibodies. Prior to the Western blot, YscQ was captured from a whole cell Y. pseudotuberculosis lysate by affinity chromatography using the same anti-YscQ polyclonal antibodies. Molecular mass markers are indicated at left.