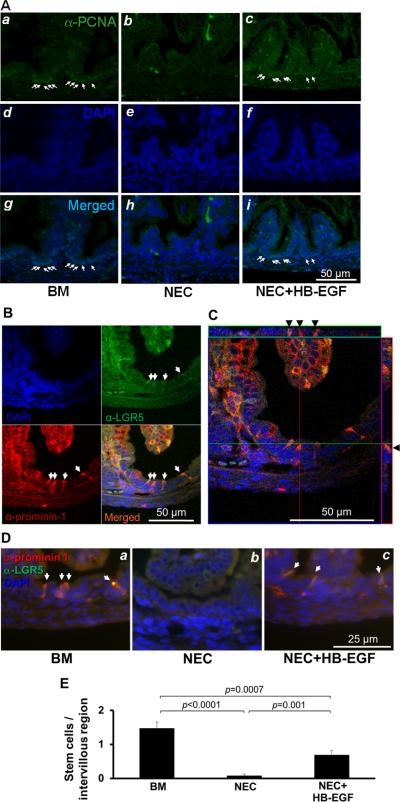
Figure 2.
HB-EGF protects proliferating ISCs and TA progenitor cells from experimental NEC. (A) PCNA immunostaining of ISCs and TA progenitor cells. Shown are representative photomicrographs from: a, d, g) a breast fed rat pup; b, e, h ) a rat pup exposed to experimental NEC; and c, f, i) a rat pup exposed to experimental NEC but treated with HB-EGF added to the feeds. Panels a-c are stained with an anti-PCNA antibody, panels d-f show DAPI nuclear staining, panels g-i show merged images. (B) Confocal microscopic images of anti-LGR5 and anti-prominin-1 double immunostaining of ISCs in the intervillous regions of uninjured breast-fed rat pups. (C) Confocal microscopic ortho-images of (B) display the intracellular anti-LGR5 and anti-prominin-1 double immunostaining (black arrowheads). The upper stripe shows the ortho-image along the green line and the stripe on the right shows the ortho-image along the red line. (D) HB-EGF protects ISCs from experimental NEC. Prominin-1 and LGR5 double immunostaining was used for detection of ISCs. Shown are representative photomicrographs from: a) a breast fed rat pup; b) a rat pup exposed to experimental NEC; and c) a rat pup exposed to experimental NEC but with HB-EGF added to the feeds. ISCs were stained with anti-LGR5 (FITC, green) and anti-prominin-1 (Cy3, red), with DAPI nuclear staining (blue). (E) Quantification of ISCs. BM, pups breast fed by surrogate mothers; NEC, pups exposed to experimental NEC; NEC+HB-EGF, pups exposed to experimental NEC but with HB-EGF added to the feeds. Values represent mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA with Tukey-Kramer pair-wise comparison test.