Figure 6.
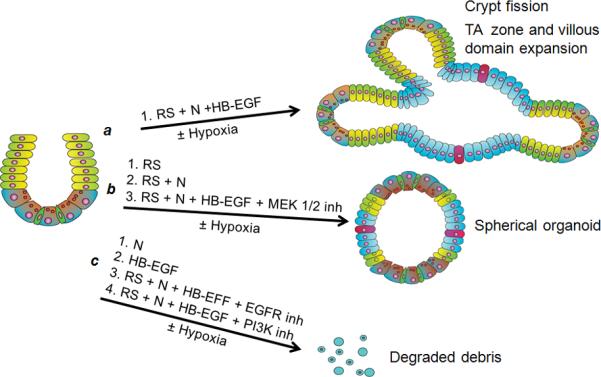
Schematic summary of ex vivo organoid culture experiments. a) In the presence of R-spondin 1 and Noggin, addition of HB-EGF leads to increased crypt-villous organoid growth, with promotion of crypt fission and TA zone/villous domain expansion. b) In the presence of R-spondin 1 alone, R-spondin 1 plus Noggin, or R-spondin 1 plus Noggin plus HB-EGF in the presence of MEK 1/2 inhibition, crypt-villous organoid growth is limited to small spherical organoids. c) In the presence of Noggin alone, HB-EGF alone, or R-spondin 1 plus Noggin plus HB-EGF in the presence of either EGFR or PI3K inhibition, crypt-villous organoid growth is completely abolished. Thus, EGFR and PI3K activation are crucial, and MEK 1/2 activation is important, in HB-EGF-mediated crypt-villous organoid growth. ISCs, green; progenitor cells in TA zone, yellow; paneth cells, brown; enterocytes, blue; goblet cells, red. N, Noggin; RS, R-spondin 1.
