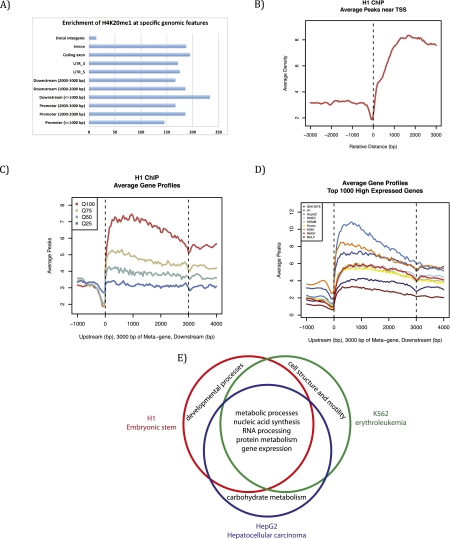
Figure 4.
Genome-wide distribution and features of H4K20me1 from the ENCODE project. Bioinformatic analysis (MACS) was used to analyze H4K20me1 genome-wide distribution from ENCODE data sets from nine different human cell lines: H1 (human ES cells), K562 (erythrocytic leukemia), GM12878 (B-lymphoblastoid), HepG2 (hepatocellular carcinoma), NHEK (normal human epidermal keratinocytes), HSMM (primary human skeletal muscle myoblasts), NHLF (normal human lung fibroblasts), Huvec (primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells), and HMEC (primary human mammary epithelial cells). (A) H4K20me1 is enriched on intragenic features in H1 cells, representative of other cell lines. (B) H4K20me1 is enriched downstream from the TSS in H1 cells, representative of other cell lines. (C) H4K20me1 is found within the gene body and is correlated best with the highly expressed genes (Q100) and less so with the lower expressed genes in H1 cells, representative of other cell lines. (D) Comparison across all nine cell lines; Q100 genes show a similar distribution, with differences in the level of enrichment. (E) Venn diagram comparing gene ontology term analysis of genes within 3 kb of an H4K20me1 peaks. Conserved genes with H4K20me1 peaks across all three cell lines are housekeeping genes required in all cell types, whereas cell-specific genes enriched with H4K20me1 are genes that are only highly expressed in that specific lineage.