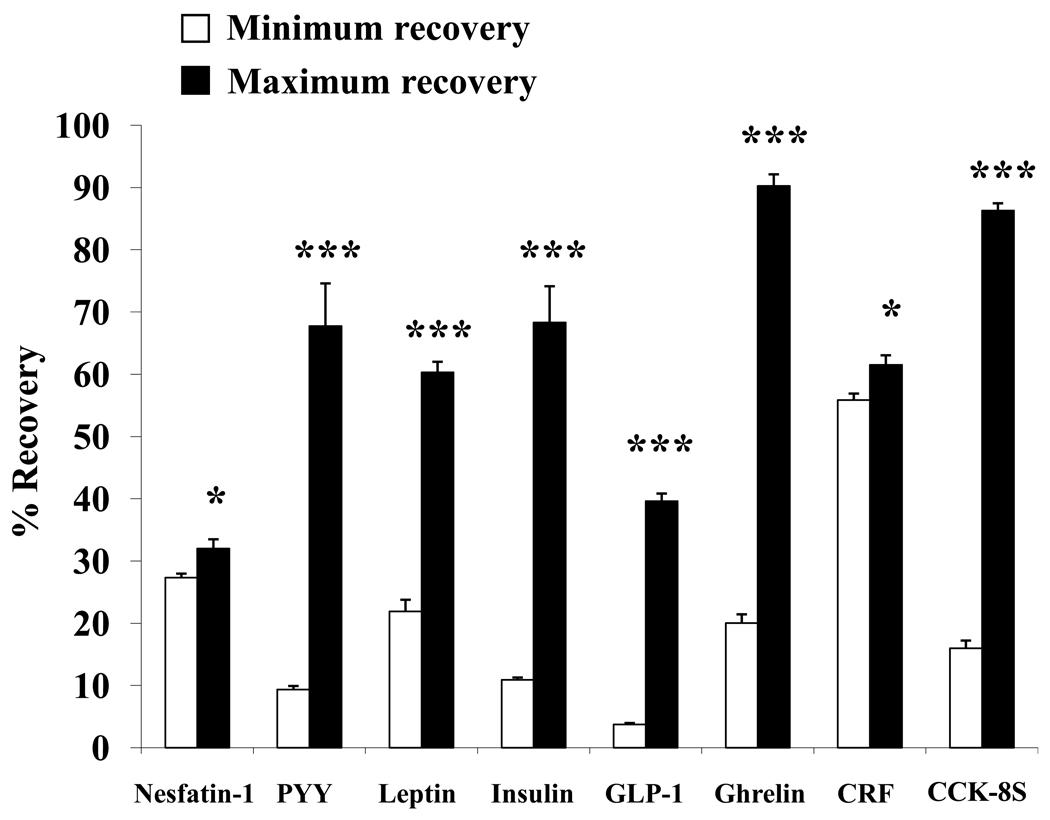
Fig. 1.
Magnitude of peptide loss assessed by percentage recovery. Depicted are recoveries of 125I-labeled peptides from their respective highest binding surface (minimum recovery, white bars) compared to the lowest (maximum recovery, black bars). Significantly higher recoveries resulted from use of borosilicate glass for nesfatin-1, PYY, leptin, GLP-1 and CRF. Polypropylene plastic yielded significantly higher recoveries for ghrelin and CCK-8S while polyallomer gave maximum recovery for insulin. The use of polystyrene plastic resulted in minimum recovery for PYY, leptin, GLP-1, CRF and CCK-8S, use of polycarbonate plastic, polypropylene plastic and flint glass resulted in lowest recoveries for nesfatin-1, insulin and ghrelin, respectively. * p < 0.05 and *** p < 0.001.