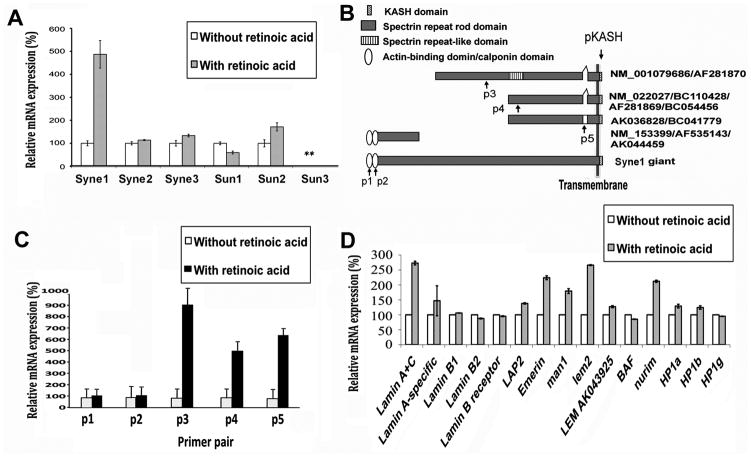
Figure 4. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of nuclear envelope components in undifferentiated and retinoic acid-differentiated ES cells.
Cultured mouse ES cells and their differentiated derivatives following retinoic acid treatment for 4 days were harvested for expression analysis by qRT-PCR of a panel of nuclear envelope components. (A) Syne and Sun isoforms were analyzed for their expression by qRT-PCR. For Synes, the primer sequences locate in the KASH domain (pKASH). Relative expression levels are shown by normalizing the expression as “100%” in undifferentiated cells. “**”, the expression level of Sun3 is too low for analysis. The increase in Syne1 expression upon cell differentiation is statistically significant (p < 0.005). (B) The structural isoforms of Syne1 are illustrated. The GENBANK assession numbers and the location of primers used in PCR are shown. (C) Syne1 isoforms were further analyzed by qRT-PCR using specific primer pairs (p1–5). The location of the primer pairs is indicated in (B) and the sequences are listed in Supplemental Table 1. (D) Additional nuclear envelope proteins as well as HP1alpha, beta, and gamma were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR. The expression of several putative housekeeping genes was also measured and serves as controls (not shown). Expression of nuclear envelope proteins at the mRNA level was normalized to hprt (which shows very little variation between ES cells and differentiated cells). Expression levels are shown by normalizing the expression as “100%” in undifferentiated cells.