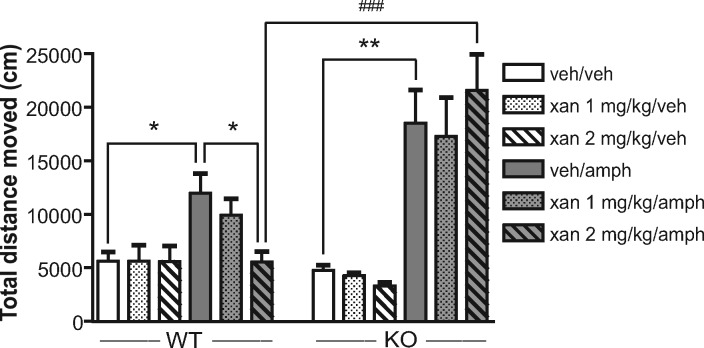
Figure 3.
Lack of attenuation of amphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion by xanomeline in D1-M4–/– mice. The effect of xanomeline (xan) on amphetamine (amph)-induced hyperlocomotion was measured after coadministration of xanomeline, vehicle (veh), and/or amphetamine (2 mg/kg, s.c.) for 2 h in an open field arena. Amphetamine induced a significant increase in locomotor activity (measured as total distance moved) in both genotypes (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs vehicle). In floxed control mice, 2 mg/kg xanomeline reversed the amphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion, but had no effect in D1-M4–/– mice (###p < 0.001 vs WT). [Reprinted with permission from Journal of Neuroscience.]85