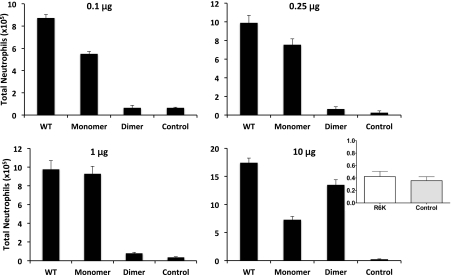
Figure 2. Neutrophil recruitment activity of CXCL8 variants.
Total neutrophils recruited into the peritoneum are plotted for each of the variants at different doses. Data are presented as mean ± sem and are from 10 to 19 animals from a total of two to four independent experiments with four to six animals/group for each experiment. One-way ANOVA was used to determine statistical significance. The recruitment of the WT compared with the monomer and dimer is significant at all doses (P<0.01), except at 1 μg between WT and monomer. The recruitment of WT and monomer compared with the control was significant at all doses (P<0.01) and of the dimer compared with control was significant only at the 10 μg dosage. Inset: The R6K mutation renders CXCL8 completely inactive, and its recruitment at 10 μg dose is similar to that of control PBS, indicating that recruitment as a result of spurious contamination or bacterial byproducts can be ruled out.