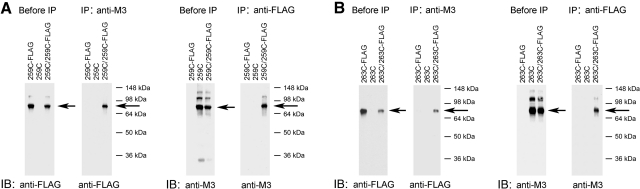
Figure 4.
Coimmunoprecipitation confirming the formation of mutant M3R homodimers. Data are shown for 2 representative mutant M3Rs, 259C and 263C. A) Coimmunoprecipitation of cross-linked 259C and 259C-FLAG mutant M3Rs. B) Coimmunoprecipitation of cross-linked 263C and 263C-FLAG mutant M3Rs. For these experiments, we first generated a modified version of the 259C and 263C mutant M3Rs in which the C-terminal recognition sequence for the anti-M3R antibody (Fig. 1) was replaced with a FLAG tag, resulting in the 259C-FLAG and 263C-FLAG constructs, respectively. Membrane samples prepared from COS-7 cells coexpressing 259C and 259C-FLAG (A) or 263C and 263C-FLAG (B) were subjected to the cross-linking procedure using 100 μM Cu-Phen as described in Materials and Methods. Solubilized membrane proteins were then incubated with the anti-M3R polyclonal antibody [immunoprecipitation (IP): anti-M3] or a monoclonal anti-FLAG antibody (IP: anti-FLAG). Subsequently, protein A-agarose was added, and the bound immunoreactive proteins were eluted and blotted with a monoclonal anti-FLAG antibody [immunoblot (IB): anti-FLAG] or the anti-M3R polyclonal antibody (IB: anti-M3) under nonreducing conditions. Western blots of membrane proteins prior to immunoprecipitation are shown in the left panels for comparison (before IP). Arrows indicate ∼80-kDa bands corresponding to the cross-linked M3R dimers. Blots shown are representative of 2 to 4 independent experiments.