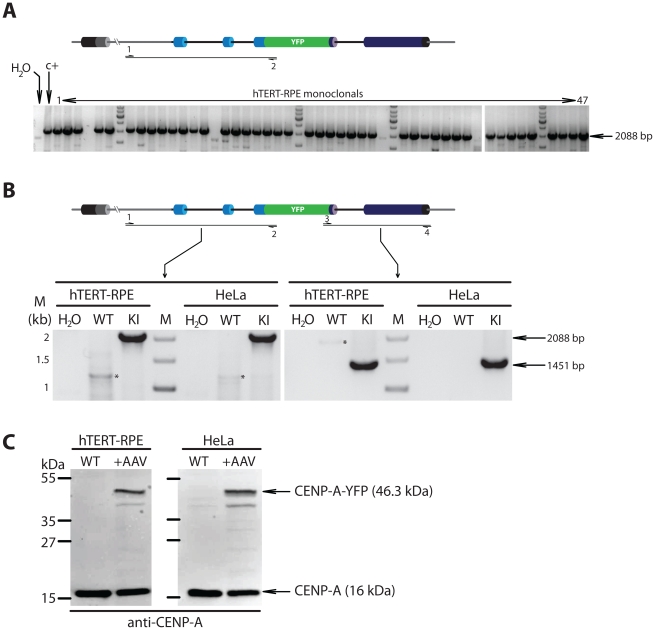
Figure 3. PCR screening and Western verification of EYFP-knockin clones.
(A) Schematic outlining PCR screening strategy. Grey regions indicate sequences outside the targeting construct. A primer set in which one primer complementary to a region outside the targeting construct and one primer inside the targeting construct (EYFP) was used to amplify a 2088 bp fragment unique to targeted clones. 47 monoclonal lines produced in the pipeline outlined in Figure 1B were screened for targeting. Water and a previously targeted HeLa clone (c+) were used as negative and positive clones respectively. (B) PCR verification of targeting. Representative clones are shown in which the left and right flanks are amplified using primer set in which one primer anneals outside the targeted area and one to EYFP sequences. Sizes of marker fragments (M) and of expected products are indicated. WT, wild type uninfected parent cells. KI, knockin clones. Asterisks indicate non-specific background products (C) Wild type hTERT-RPE or HeLa or targeted knockin clones were processed for SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with an anti-CENP-A antibody revealing novel high molecular weight CENP-A-EYFP fusion protein in targeted clones only. Proteins from both the targeted CENP-A-EYFP and untagged CENP-A alleles are detected.