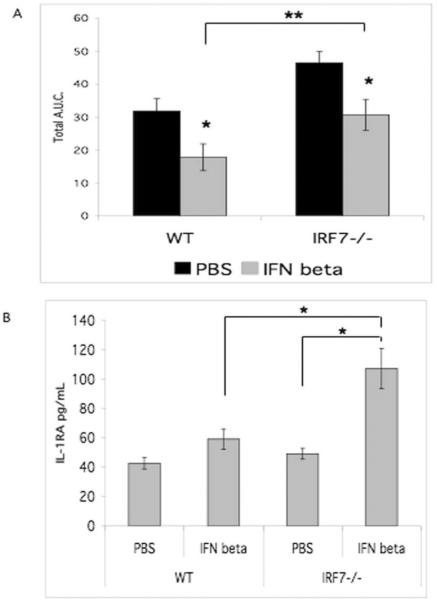
Figure 3.
IFNβ treatment in Irf7−/− mice effectively decreased arthritis. A. Irf7−/− and WT mice were injected with serum on day 0 and 2. Mice were injected IP daily with IFNβ 1000 IU or PBS. Treatment of the Irf7−/− mice with replacement IFNβ decreased the amount of arthritis to WT levels. The inhibition of arthritis by IFNβ treatment in Irf7−/− mice was significant and IFNβ treatment also decreased arthritis in WT mice (*p<0.05). Arthritis was significantly increased in Irf7−/− mice despite IFNβ treatment (**p<0.05). B. Serum IL-1RA was increased in Irf7−/−mice treated with IFNβ compared with control treatment (*p<0.03). IL-1RA was significantly higher in Irf7−/−serum compared with WT after treatment with IFNβ (*p<0.03).