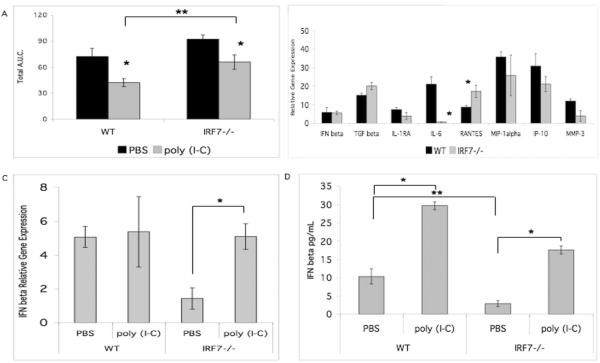
Figure 4.
Treatment with poly (I-C) decreased arthritis in the passive serum transfer model. A. Irf7−/− and WT mice were injected with serum on day 0 and 2. Treatment was performed with IP injection of poly (I-C) or PBS on day 0 and 2. Both WT and Irf7−/− poly (I-C) treatment groups had less paw swelling (*p<0.05). Treatment with poly (I-C) decreased the amount of arthritis in Irf7−/− to WT levels. Irf7−/− mice had increased arthritis compared with WT despite treatment with poly (I-C) (**p<0.05). B. Poly (I-C) mediated induction of gene expression in the synovial tissue of Irf7−/− mice demonstrated that IFNβ gene expression was restored to WT levels. C. Poly (I-C) treatment in Irf7−/− mice increases IFNβ gene expression to WT levels (*p<0.001). D. IFNβ protein by ELISA was increased in the sera of arthritic WT and Irf7−/− mice treated with poly (I-C) (*p<0.05). Baseline IFNβ in serum is decreased in Irf7−/− mice (**p<0.05).