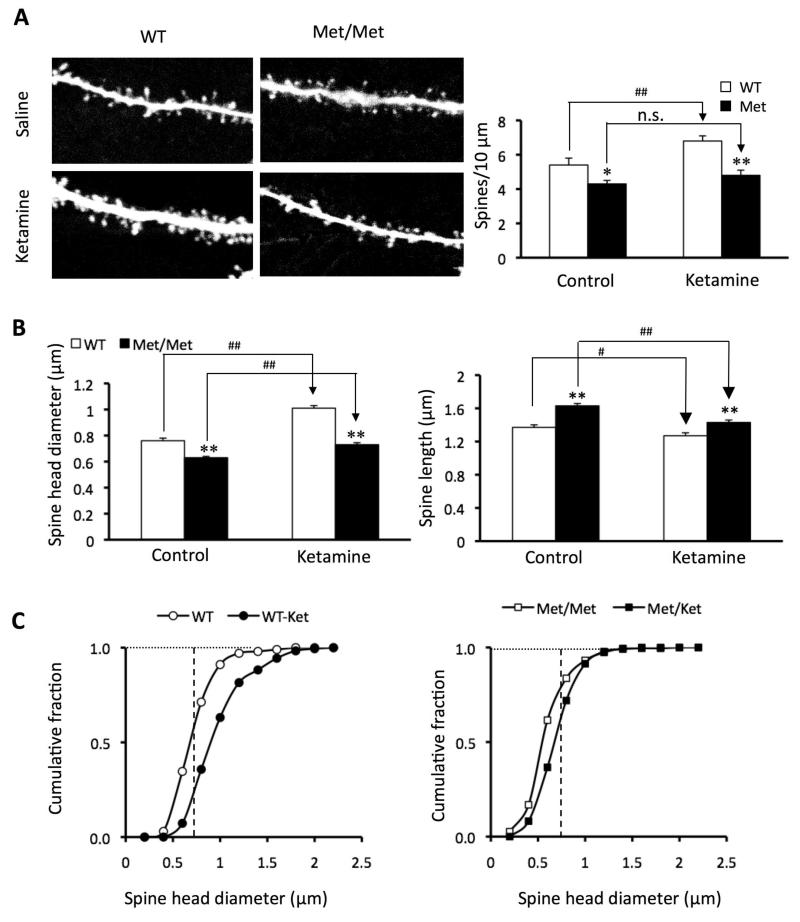
Figure 4. Synaptogenic effects of ketamine are blunted in BDNF Val66Met knock-in mice.
Mice received ketamine injections (10 mg/kg, i.p.). (A) Representative images of high zoom Z-stack projections of proximal segments of the apical tuft dendrites. Bar graph (right) shows decrease in spine density in Met allele group; this deficit was not reversed by ketamine treatment (p<0.05*/#; p<0.01**/##). (B) Bar graphs showing decrease in mean spine head diameter and increase in spine length in apical tuft Met group. (C) Cumulative fraction curves for the tuft spine diameter. Plot on left shows a marked increase in population of large mushroom spines in the ketamine group compared to WT (>0.75 μm diameter; dashed line); plot on right shows virtually no ketamine-induced increase in mushroom spines (>0.75 μm) in Met/Met mice as compared to WT mice. Spine analysis was performed using Neurolucida Explorer, version 9; results are given as mean ± SEM.