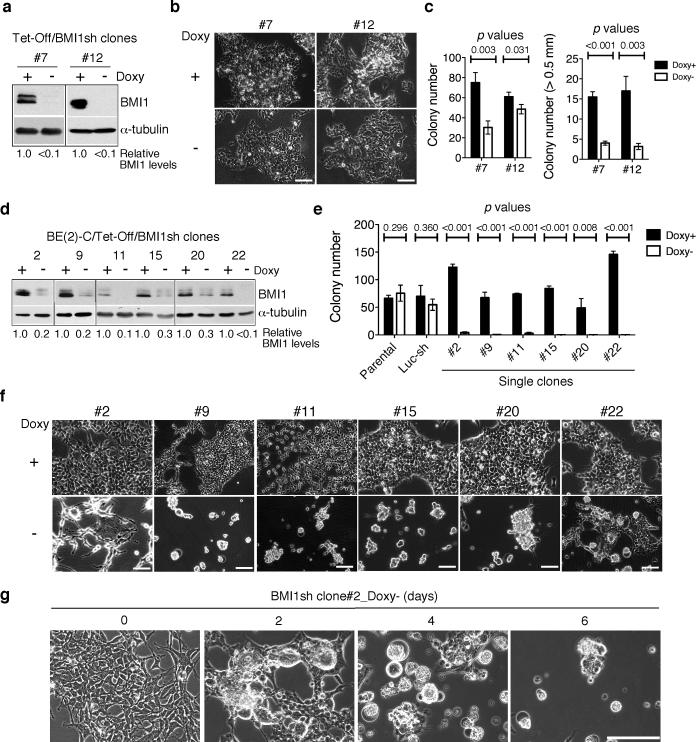
Figure 1.
Individual BE(2)-C neuroblastoma cells display differential sensitivities to BMI1 knockdown. a, Immunoblot analysis of BMI1 levels in clone-7 and -12 cells cultured in the presence or absence of doxycycline (Doxy) for 3 days. BMI1 levels were quantified against α-tubulin and are presented as the fraction of the BMI1 level in the presence of Doxy. b, Phase contrast imaging of clone-7 and -12 cells cultured in the presence or absence of Doxy for 10 days. Scale bars, 100 μm. c, Soft agar clonogenic assay of clone-7 and -12 cells in the presence or absence of Doxy. Numbers of total colonies and of the colonies that were larger than 0.5 mm were determined (error bars, s.d., n=3). d, Immunoblot analysis of BMI1 levels in BMI1-sensitive clones cultured in the presence or absence of Doxy for 3 days. BMI1 levels were quantified against α-tubulin and are presented as the fraction of the BMI1 level in the presence of Doxy. e, Soft agar clonogenic assay of parental and luciferase shRNA-expressing BE(2)-C cells, and BMI1-sensitive clones in the presence or absence of Doxy. Numbers of total colonies were determined (error bars, s.d., n=3). All quantitative data from soft agar assays were analyzed using two-tailed Student's t-test with the p values indicated. f, Phase contrast imaging of BMI1-sensitive clones cultured in the presence or absence of Doxy for 3 days. g, Phase contrast imaging of the clone-2 cells cultured in the absence of Doxy for 0-6 days. Scale bars (f-g), 100 μm.