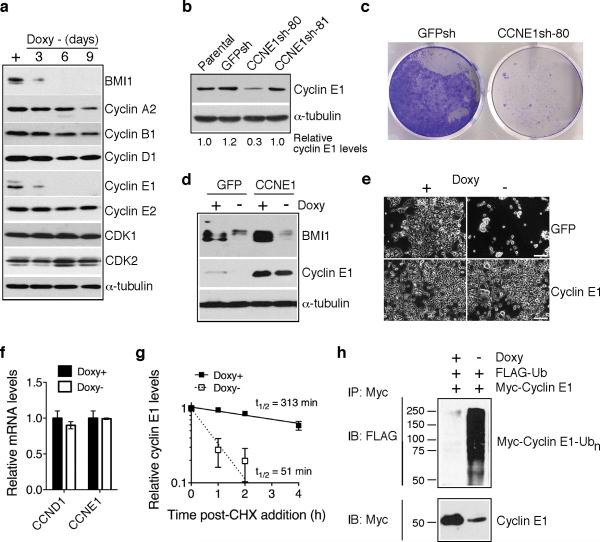
Figure 2.
BMI1 suppresses cell death by stabilizing cyclin E1. a, Immunoblot analysis of cyclins and CDKs in pooled BMI1-sensitive clones following BMI1 knockdown. α-tubulin levels are shown as loading control. b, Immunoblot analysis of cyclin E1 levels in BE(2)-C cells either uninfected (parental) or infected with retroviruses expressing shRNA sequences against GFP (GFPsh) or different regions of CCNE1 (CCNE1sh-80 and -81). Cyclin E1 levels were quantified against α-tubulin and are presented as the fraction of the cyclin E1 level in parental cells. c, Crystal violet staining of BE(2)-C cells expressing either GFPsh or CCNE1sh-80. d, Immunoblot analysis of BMI1 and cyclin E1 levels in pooled BMI1-sensitive clones infected with retroviruses expressing either GFP or Myc-cyclin E1 and cultured in the presence or absence of Doxy for 3 days. α-tubulin levels are shown as loading control. e, Phase contrast imaging of pooled BMI1-sensitive clones expressing either GFP or Myc-cyclin E1 and cultured in the presence or absence of Doxy for 6 days. Scale bars, 100 μm. f, qRT-PCR analysis of CCND1 and CCNE1 mRNA levels in pooled BMI1-sensitive cells cultured in the presence or absence of Doxy for 3 days (error bars, s.d., n=3). g, Quantification of cyclin E1 half-life in pooled BMI1-sensitive clones cultured in the presence or absence of Doxy for 3 days. Samples were collected at various time points following addition of cycloheximide (CHX) for immunoblot analysis. Cyclin E1 levels were quantified against α-tubulin and are presented as the fraction of the initial levels at time zero (error bars, s.d., n=4). h, In vivo ubiquitination assay of pooled BMI1-sensitive cells cultured in the presence or absence of Doxy for 3 days and co-transfected with Flag-ubiquitin and Myc-cyclin E1 expression plasmids. Polyubiquitinated cyclin E1 was detected by immunoprecipitation of Myccyclin E1, followed by immunoblotting for Flag-ubiquitin.