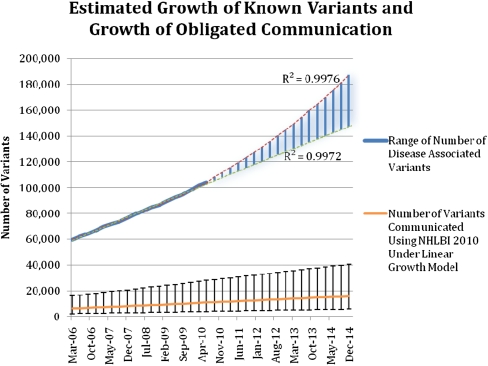
Figure 1.
Estimated growth of the knowledge base of disease-associated variants and the number of variants that may meet the threshold for recommended communication to research participants. The quarterly totals of variants from the Human Gene Mutation Database and the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) Catalog of Published Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) over 4 yr were the basis for creating logarithmic (lower line) and exponential (upper line) regressions (R2 = 0.9976, 0.9972). The range of likely growth is highlighted in blue between these two lines. These regressions were extrapolated to estimate the possible growth rates of disease-associated genetic variants in the following 4 yr. Linear growth rate data (R2 = 0.9977) were also used to extrapolate the estimated number of variants that would be shared with research participants under the 2010 guidelines for disclosure. Bars, 95% confidence intervals for each quarterly estimate.