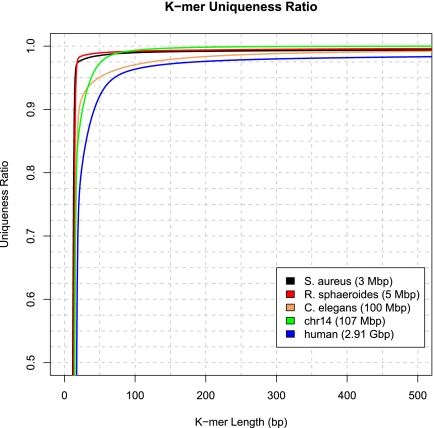
Figure 4.
K-mer uniqueness ratio for the three genomes assembled in GAGE: the bacteria S. aureus and R. sphaeroides and human chromosome 14. The ratio is defined as the percentage of a genome that is covered by unique (i.e., non-repetitive) DNA sequences of length K. Shown for comparison are the k-mer uniqueness ratios for the full human genome and for the nematode C. elegans.