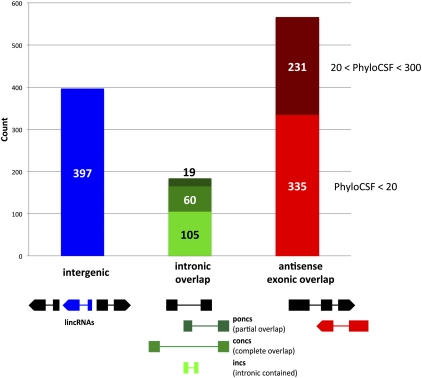
Figure 3.
Classification of lncRNAs. Numbers of lncRNAs in each of the three main classes, as defined by their genomic location relative to neighboring or overlapping genes. Intergenic lncRNAs (blue; lincRNAs) have no overlap with any gene. lncRNAs with intronic overlap (green) are defined as loci that have overlap with another transcribed locus but no exon–exon overlap (no overlap between the mature lncRNA transcript with exons of the overlapping locus). They are on either the same or the opposite strand relative to the overlapping gene and can be partitioned into intronic contained lncRNAs (incs, light green; the lncRNA is contained within the transcribed region of another locus), completely overlapping lncRNAs (concs, green; the other locus is contained within the transcribed region of the lncRNA locus), and partially overlapping lncRNAs (poncs, dark green; neither inc nor conc, but at least one exon of the lncRNA has overlap with an intron of another locus). LncRNAs with antisense exonic overlap (red) have at least one exon that overlaps with an exon of a protein-coding transcript on the opposite strand; they can be partitioned into those identified via the general pipeline (PhyloCSF < 20, light red) and those rescued via the antisense pipeline (20 < PhyloCSF < 300, dark red). A scheme of the position of the lncRNA gene (in color) relative to neighboring or overlapping gene(s) (black) is shown at the bottom.