Figure 3.
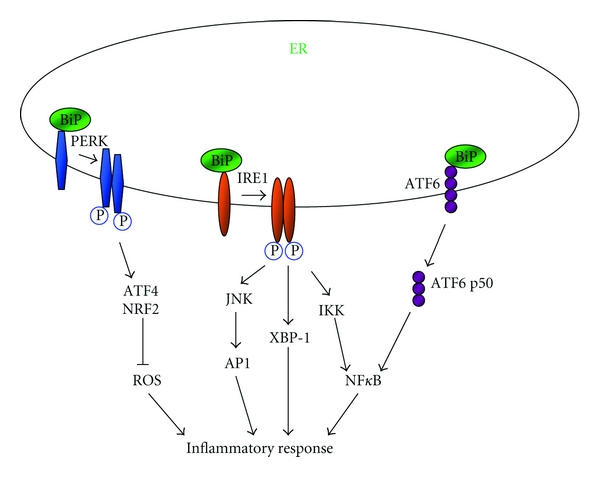
The possible implication of UPR in inflammatory response. UPR is associated with inflammation via a variety of mechanisms involving ROS, JNK, and NFκB. PERK promotes ATF4 and NRF2, which then suppress ROS production by activating antioxidant pathway. Upon activation, IRE1/TRAF2 recruits IKK, leading to the phosphorylation of IκBα and subsequent activation of NFκB. IRE1/TRAF2 can also activate AP1, resulting in the activation of JNK. XBP-1 induced by IRE1 can further induce the expression of various genes implicated inflammation. Furthermore, ATF6, the other axis of UPR signaling, can promote inflammation via activating NFκB.
