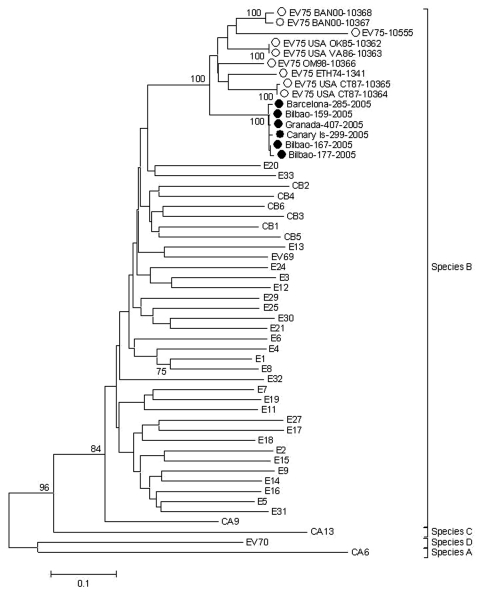
Figure.
Phylogenetic analysis of complete VP1 sequences of Spanish enterovirus (EV) isolates (GenBank accession nos. DQ468137–DQ468142), the new proposed EV75 sequences (AY556063–AY556070 and AY919545), and prototype EV sequences (echovirus [E] 5, AJ241425; E31, AJ241435; E2, AF081315; E15, AJ241429; E14, AJ241428; E17, AF081330; coxsackie B virus [CBV] 2, AF081312; E26, AJ241433; E27, AF081338; E1, AJ241422; E8, AF081325; E4, AF081319; E21, AF081334; E30, AF081340; E25, AF081336; E29, AJ241434; CBV5, AF114383; CBV6, AF081313; E13, AF081327; EV69, AF081349; E24, AJ241432; E33, AF081346; E3, AF081316; E12, X77708; CBV3, M16572; CBV1, M16560; E6, AF081322; coxsackie A virus [CAV] 9, D00627; E16, AY302542; E9, AF524866; E7, AJ241426; E32, AF081345; E19, AJ241430; E11, AF081326; CBV4, X05690; E18, AF081331; E20, AJ241431; EV70, D17602; CAV6, AF081297; CAV13, AF081303; EV74, AY208118). Phylogenetic trees were constructed with the neighbor-joining method (MEGA version 3.0, available from http://www.megasoftware.net) with Kimura 2-parameter substitution model. Significance of phylogenies was estimated by bootstrap analysis with 1,000 pseudoreplicate datasets. Closed and open circles show Spanish and previously reported EV75 isolates, respectively.