Figure A2.
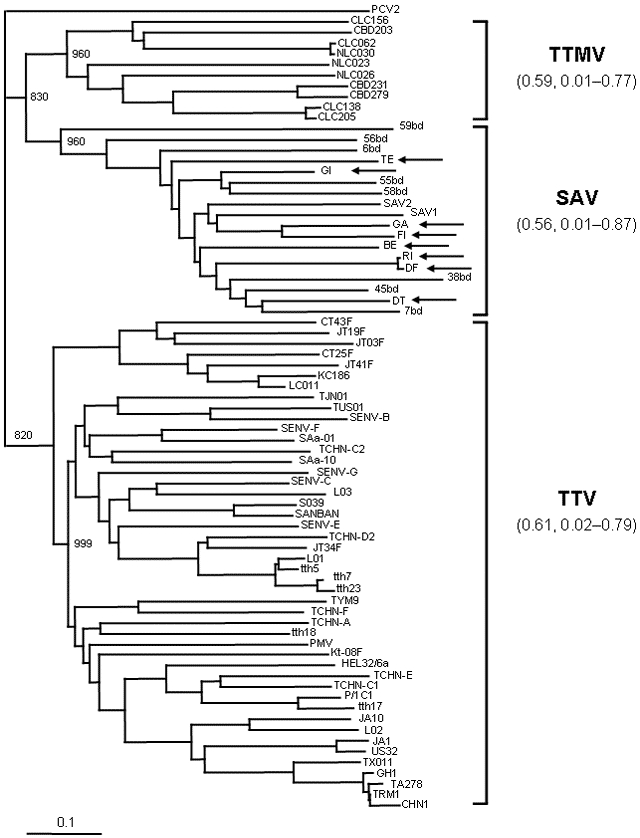
Amino acid sequences of the small anellovirus (SAV) obtained in the present study (arrows show accession nos. DQ409192 to DQ409199). GI, TE, and GA were from healthy donors; FI, RI, BE, DF, and DT were from hepatitis C patients. Evolutionary relationships between and within the 3 anelloviruses, torquetenovirus (TTV), torquetenominivirus (TTMV), and small anellovirus (SAV) are shown. Analysis is based on the 18 amino acid (aa) sequences of SAV above (75–104 aa), 46 open reading frame 2 (ORF2) amino acid sequences representative of the 5 TTV genogroups (96–104 aa), and 10 ORF2 amino acid sequences of TTMV (92–95 aa). Branching pattern was obtained by the FastME algorithm included in DAMBE software package (version 4.2.13). Bootstrap resampling was used to test the robustness of the tree, and bootstrap values >800 of 1,000 replicates are shown at the major branch points. The tree was drawn by the Treeview software (version 1.6.6). The ORF2 (110 aa) of porcine circovirus 2 was used as outgroup. Mean and range percentage amino acid distances within each of the 3 anelloviruses are shown in parentheses next to the virus names. Scale bar indicates the estimated number of amino acid substitutions per site.
