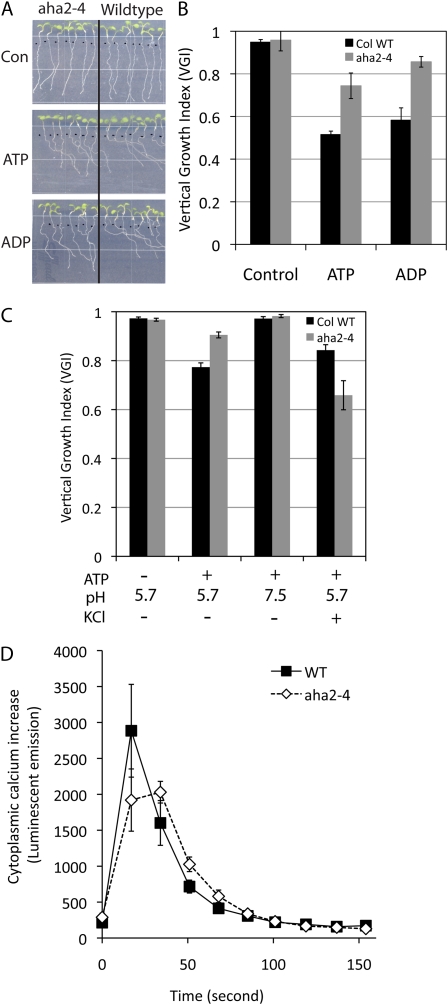
Figure 5.
Root tropism of wild-type and aha2 mutant plants in the presence of ATP. A, Root tropism of wild-type and aha2 mutant roots in the presence of ATP or ADP. Seedlings were vertically germinated on control medium (one-half-strength MS, 1% Suc, pH 5.7) for 3 d and transferred to control medium, medium with 200 μg mL−1 ATP, or medium with 200 μg mL−1 ADP. After vertical incubation for an additional 4 d, images were captured and the degree of vertical root growth of wild-type and aha2-4 mutant plants was quantified as shown in B. B, Vertical growth index of wild-type (WT) and aha2-4 mutant plants in response to ATP or ADP. Vertical growth index, described by Vicente-Agullo et al. (2004), is defined as the ratio between a vertical projection of the base-to-tip chord and the root length (Supplemental Fig. S6). C, Effect of high external pH and potassium on ATP-induced root curving. Root tropism in response to ATP was examined with plants grown on medium (one-half-strength MS, 1% Suc) adjusted to pH 7.5 or supplied with 50 mm KCl. D, ATP-induced cytoplasmic calcium increase in wild-type and aha2-4 mutant seedlings. ATP at 1 mm concentration was added to elicit cytoplasmic calcium elevation. Data are shown as averages of 10 seedlings per genotype. [See online article for color version of this figure.]