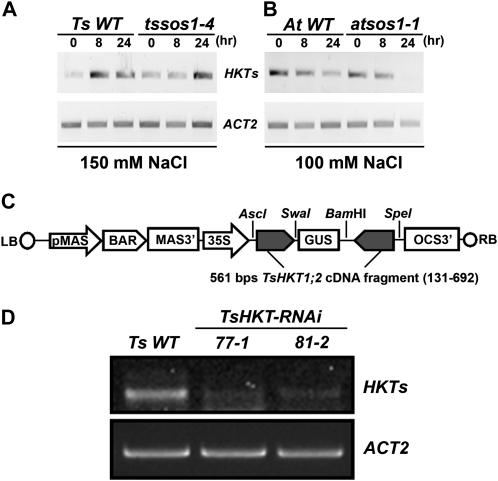
Figure 2.
Expression of HKT homologs and construction of T. salsuginea TsHKT-RNAi transgenic plants. A and B, HKT expression patterns were analyzed with semiquantitative RT-PCR in T. salsuginea (A) and Arabidopsis (B). Two-week-old T. salsuginea and 10-d-old Arabidopsis seedlings were treated with 150 and 100 mm NaCl, respectively, for the indicated times. Compared are a T. salsuginea Shandong line transformed with the empty RNAi vector (Ts WT) and Arabidopsis Col-gl1 (At WT) and their respective mutant lines with compromised SOS1 expression (tssos1-4 and atsos1-1). Actin (ACT2) is used as a reference transcript. C, Diagrammatic representation of the TsHKT-RNAi construct. BAR, Bialaphos resistance; LB, left border; MAS3′, mannopine synthase transcriptional terminator; OCS-3′, octopine synthase transcriptional terminator; pMAS, mannopine synthase promoter; RB, right border. D, TsHKT expression was inhibited in T. salsuginea lines transformed with the TsHKT-RNAi construct. Shown are two representative TsHKT-RNAi transgenic lines (77-1 and 81-2) in comparison with the vector control (Ts WT).