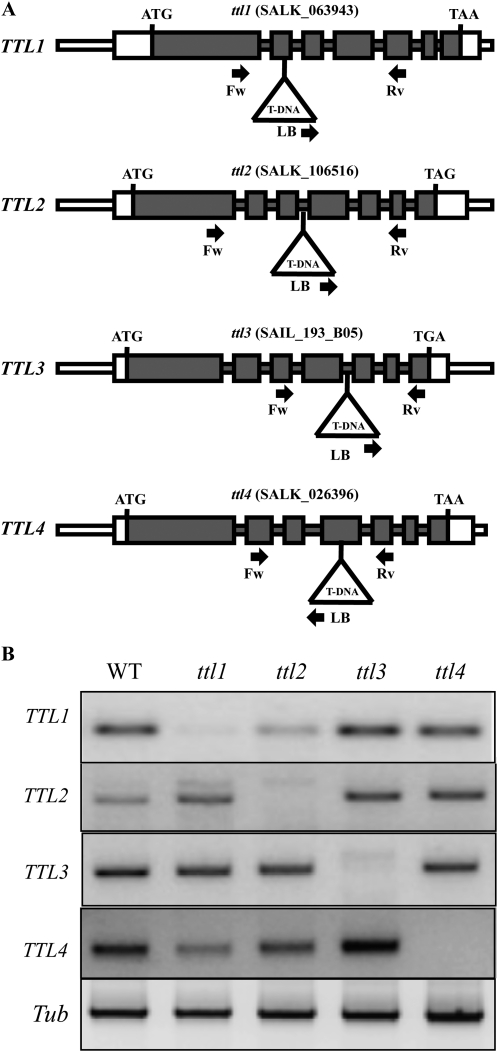
Figure 4.
Molecular characterization of ttl mutants. A, ttl1, ttl2, ttl3, and ttl4 mutant alleles. The corresponding T-DNA line from SALK is indicated at the top. Gray boxes represent exons, and lines represent introns. ATG and stop codons are indicated. White boxes indicate the 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions. T-DNA insertion sites (not drawn to scale) are represented by triangles. The primers used for PCR genotyping are indicated by arrows (see “Materials and Methods” for primer sequences). LB, Left border. B, Expression analysis of the four TTL genes in the wild type (WT) and ttl mutants by RT-PCR. RNA was extracted from flowers, which is the only tissue where TTL2 expression was detected. The gene-specific primers designed to amplify cDNA fragments are detailed in “Materials and Methods.” The tubulin gene (Tub) was used as a positive control for the RT-PCR.