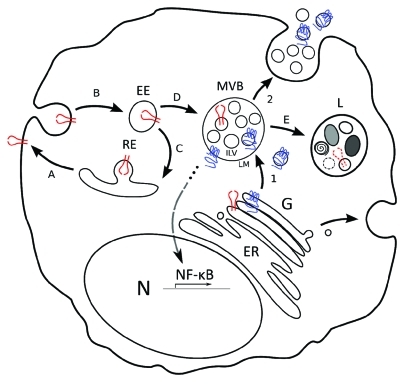
Figure 1.
Model for LMP1 trafficking and signaling as compared with EGFR. Model that highlights the distinction between latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1, in blue) trafficking via multivesicular bodies (MVB) into exosomes and Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR, in red) trafficking and degradation in lysosomes. (1) LMP1 is synthesized in the ER and traffics through the Golgi (G). Subsequently, LMP1 traffics to and accumulates in microdomains of the limiting membrane (LM) of multivesicular bodies (MVBs). Inward budding of microdomains that contain LMP1 form intraluminal vesicles (ILVs). (2) ILVs that contain LMP1 are secreted as exosomes upon fusion of the LM with the plasma membrane (PM). In all steps from Golgi to LM the C-terminus of LMP1 that mediates NF-kB signaling is exposed to the cytoplasm. EGFR in contrast traffics to the plasma membrane (A), is ubiquitinated and internalized in early endosomes (B). A fraction is re-expressed at the PM via recycling endosomes (C), the remainder is incorporated in MVBs (D) and targeted for degradation (E) by fusion with lysosomes (L). Both PM associated and internalized EGFR signal after EGF binding.