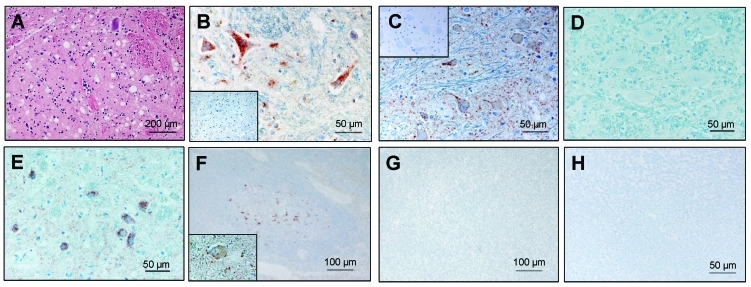
Figure 1.
Histopathologic and immunohistochemical analyses. A) Spongiform lesions; B) partially proteinase K–resistant prion protein (PrPsc) deposits detected by immunohistochemistry (monoclonal antibodies [MAb] F99/97.6.1 diluted 1:500) in the nucleus of the solitary tract (STN) in the zebu under investigation. C–E) Comparative immunohistochemistry with MAb P4 (1:800) in the olivary nuclei of the zebu (C), a bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE)-positive cow (D), and a scrapie-positive sheep (E). Insets show control tissue slides of BSE-negative cattle. F–H) Immunohistochemistry for PrPsc in lymphoid tissue of the zebu (H, mediastinal lymph node), and a BSE-negative cow (G, mandibular lymph node) with MAb L42 (R-biopharm, 1:800). A retropharyngeal lymph node of a scrapie-affected sheep (F) and a brainstem tissue slide of the zebu (F, inset) served as positive controls. Pretreatment of the tissue slides comprised a proteinase K–digestion step (5 μg/mL, 15 min, 37°C).