Figure 7. A model for context specific KRAS dependency in colon cancers.
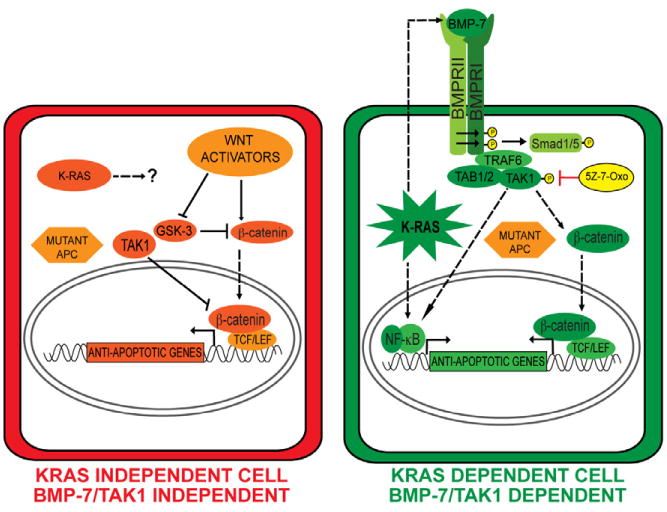
In KRAS-independent colon cancers, APC loss of function results in hyperactivation of canonical Wnt signaling through stabilization of β-catenin in cooperation with upstream Wnt activators. TAK1 can be a negative regulator of canonical Wnt signaling in these cells. In KRAS-dependent cells, oncogenic KRAS upregulates BMP-7 expression/secretion, activating the BMP receptor resulting in TAK1 activation. KRAS and TAK1 in these cells are activators of Wnt signaling by promoting β-catenin nuclear localization, which is stabilized by virtue of APC loss of function mutations. KRAS-mediated anti-apoptotic signaling could also be facilitated by NF-κB activation. Dashed lines represent unknown molecular interactions.
See also Figure S6.
