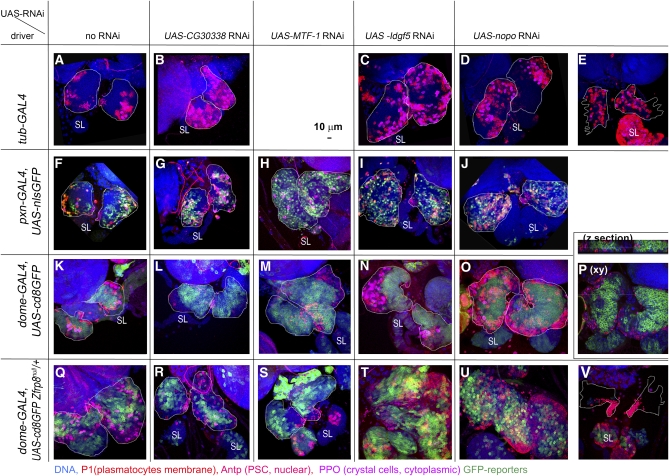
Figure 5 .
Knockdown phenotypes of Zfrp8 modifiers. Confocal projections of lymph glands obtained from the crosses of the three drivers [tub-GAL4 (A–E); pxn-GAL4,2XUAS-nlsGFP (CZ cells, nuclear green, F–J), and dome-GAL4, UAS-cd8GFP (MZ cells, membrane green, K–P)] to UAS-RNAi lines of CG30338 (B, G, L, R), MTF-1 (H, M, S), Idlg5 (C, I, N, T), and nopo (D, E, J, O, P, U, V). Drivers crossed with wild type (A, F, K) show normal MZ-CZ organization and hemocyte differentiation. (Q) dome-GAL4, UAS-cd8GFP combined with heterozygous Zfrp8null shows lymph gland enlargement, similar to that of Zfrp8null/+, and increase in dome-positive cells intermingled with CZ prohemocytes. The lymph gland overgrowth is suppressed when CG30338 (R) or MTF-1 (S) are knocked down in MZ, whereas overgrowth is enhanced when Idgf5 (T) or nopo (V) are depleted. nopo knockdown in trans to Zfrp8null/+ also causes disintegration of primary lobes in late third-instar larvae (V). Primary lobes (outlined by white dotted line) are identified by their anterior position and presence of PSC (anti-Antp, nuclear red). Secondary lobes (SL) show excessive growth and differentiation in most nopo knockdown lymph glands (E, J, U, V). Plasmatocytes are stained with P1 antibody (membrane, red) and crystal cells with anti-PPO2 (cytoplasmic, pink). DNA is shown in blue. Scale bar is 10 μm.