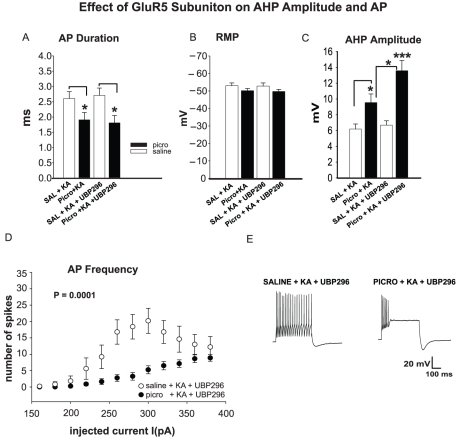
Figure 2. Increased AHP Amplitude and decreased AP firing in the presence of kainic acid is dependent on the GluR5 subunit.
A, Bath application of UBP296 does not change AP duration and RMP (B) of fast-spiking interneurons from PICRO-treated rats compared to experimental conditions with no drug. C, D, UBP296 application is associated with an increase of AHP and decrease of AP firing rate in SO of CA2/3 fast-spiking interneurons from PICRO-treated rats. A significant increase of AHP amplitude has been observed when comparing SAL+KA+UBP296 versus PICRO+KA+UBP296 groups (p<0.001). UBP296 failed to induce any electrophysiological changes in control rats (A–E). E, This panel shows representative traces recorded before and after application of UBP296 in PICRO versus SAL rats. Results are presented as the mean ± SEM. *p<0.05 or ***p<0.001 versus saline.