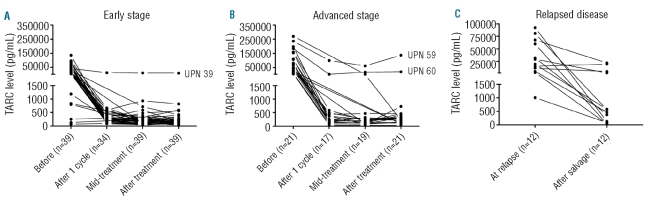
Figure 3.
Plasma TARC dynamics in early and advanced stage newly diagnosed and relapsed cHL patients. (A) Plasma TARC dynamics before treatment, after one ABVD cycle, at mid-treatment (after 2 ABVD cycles) and after treatment among 39 newly diagnosed early stage cHL patients. All responsive patients had a decline in plasma TARC to normal range levels, while one non-responsive patient (UPN 39) had persistent high plasma TARC levels and could already be identified after one cycle of ABVD. (B) Plasma TARC dynamics before, after one ABVD or (e)BEA-COPP cycle, at mid-treatment (after 4 ABVD or 4 (e)BEACOPP cycles) and after treatment among 21 newly diagnosed advanced stage cHL patients. Again, the 2 non-responsive (UPN 59 and 60) patients could be distinguished from all responsive patients already after one cycle of chemotherapy by persistent high plasma TARC levels. (C) TARC dynamics at relapse and after relapse treatment in 12 relapsed cHL patients. All 12 relapsed patients had moderate to high elevated plasma TARC levels at relapse. Four final non-responsive patients had persistent high plasma TARC levels after second-line treatment, while all responsive patients had a decline in plasma TARC to normal range levels.