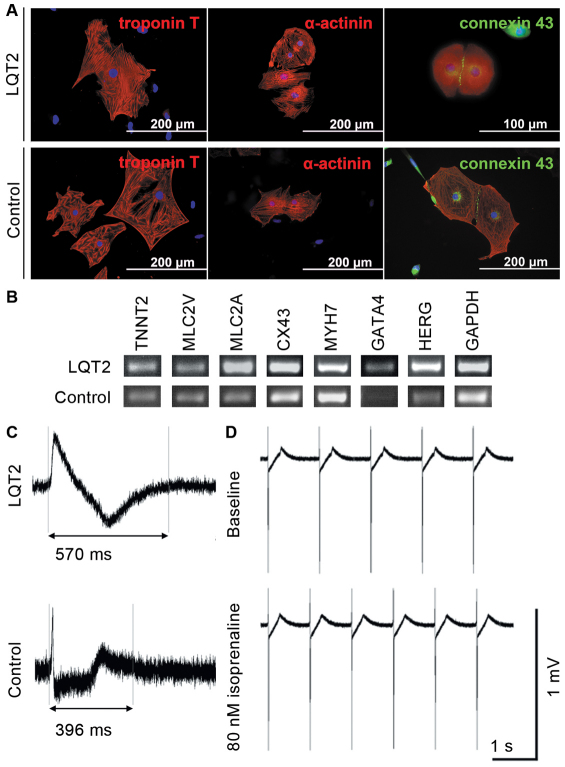
Fig. 3.
The expression of cardiac markers in iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes and the electrical properties of the cells. (A) Immunocytochemical staining of different cardiac markers: troponin T and α-actinin are shown in red; green indicates connexin-43 and blue represents DAPI-staining for nuclei. The expression was similar in LQT2-specific and control cells, and there were no line-specific differences in the expression of cardiac proteins. (B) The expression of a larger repertoire of cardiac markers was also studied, with RT-PCR showing that the iPSC-derived cardiac cells manifest cardiac properties. TNTT2, MLC2V, MLC2A, Cx-43, MYH7, GATA4 and HERG were present in the cells at the mRNA level. (C) Electrical properties of the cells were studied with MEA, which revealed the differences between LQT2-specific and control cells. FPD was significantly longer in LQT2-specific cardiomyocytes than in control cardiac cells. However, all lines evince the typical electrical properties of cardiomyocytes. (D) LQT2-specific cardiomyocytes showed increased chronotrophy when challenged with isoprenaline, a β-adrenergic agonist.