Fig. 3.
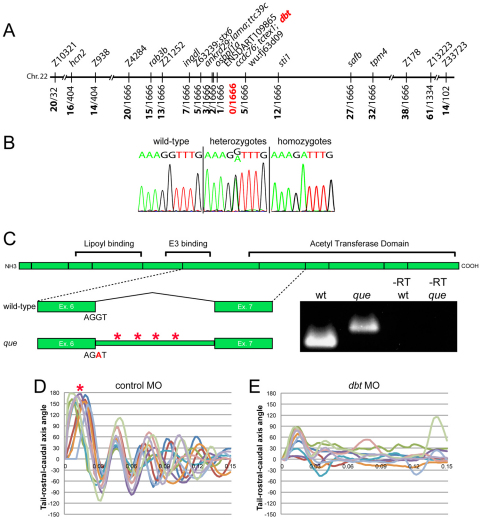
Theque gene encodes dihydrolipoamide branched-chain transacylase E2 (Dbt), a subunit of the BCKD complex. (A) que maps to a 0.36 cM interval on chromosome 22. Molecular markers are shown at the top and the number of recombinants out of the number of meiotic events are shown at bottom. dbt was positioned within the zero recombinant interval. (B) Chromatogram sequence traces of dbt from wild-type, hetero-and homozygous mutant larvae. The nucleotide substitution at the exon-intron boundary (G to A) can be observed in hetero- and homozygotes. (C) A schematic of the dbt protein is shown with the boundaries between exons indicated as vertical lines. Protein domains, including the acetyl transferase domain, are also shown. Below, the wild-type splice pattern is illustrated, with protein-coding exon 6, the sequence at the splice site, the intervening intron, and protein-coding exon 7 depicted. The que mutant splicing pattern is also illustrated, including the nucleotide substitution, which results in a failure to remove the intron. The intron contains four stop codons (asterisks). RT-PCR results using mRNA from wild type, que mutants and –RT controls are also shown using primers targeted towards exon 6 and exon 7. A larger DNA product, containing intron sequence, can be observed using mRNA isolated from que mutants. (D,E) Ten kinematic traces are shown for embryos injected with (D) the control morpholino or (E) a dbt translation-blocking morpholino. Embryos injected with the control morpholino perform C-bends (asterisk) and normal swimming behavior. dbt morphant embryos demonstrate abnormal swimming behavior and few large amplitude body bends, similar to que mutants.