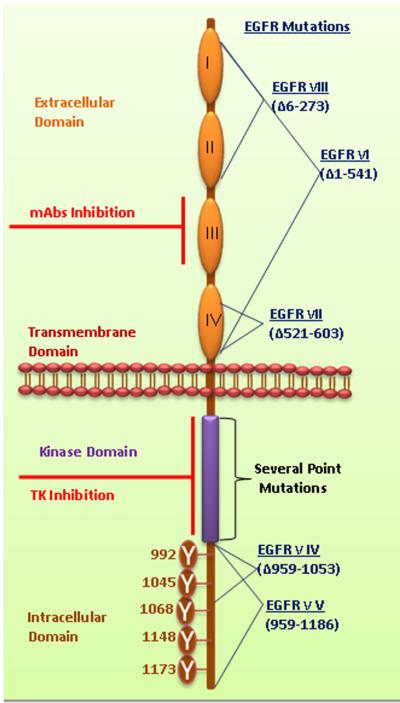
Figure 1a. Structural elucidation of EGFR.
EGFR family members share a common domain arrangement comprised of a cysteine-rich extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain and an intracellular tyrosine kinase domain with several phosphorylation sites. The extracellular domains are subdivided and numbered as I-IV. Numerous phosphorylation sites were mentioned in cytoplasmic domain of EGFR. Monoclonal antibodies target the extracellular domain III. The small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors bind with the ATP binding pockets in the tyrosine kinase domain. Several deletion mutations occur in the EGFR such as EGFRvI (AAΔ1–541), EGFRvIII (AAΔ6–273), EGFRvII (AAΔ521–603), EGFRvIV (AAΔ959–1053) and EGFRvV (AAΔ959–1186). Additionally, several point mutations occur in TK domain of EGFR. Furthermore, the details of EGFR mutations were discussed by Kuan et al.2001 [116]. (AAΔ amino acid deletion).