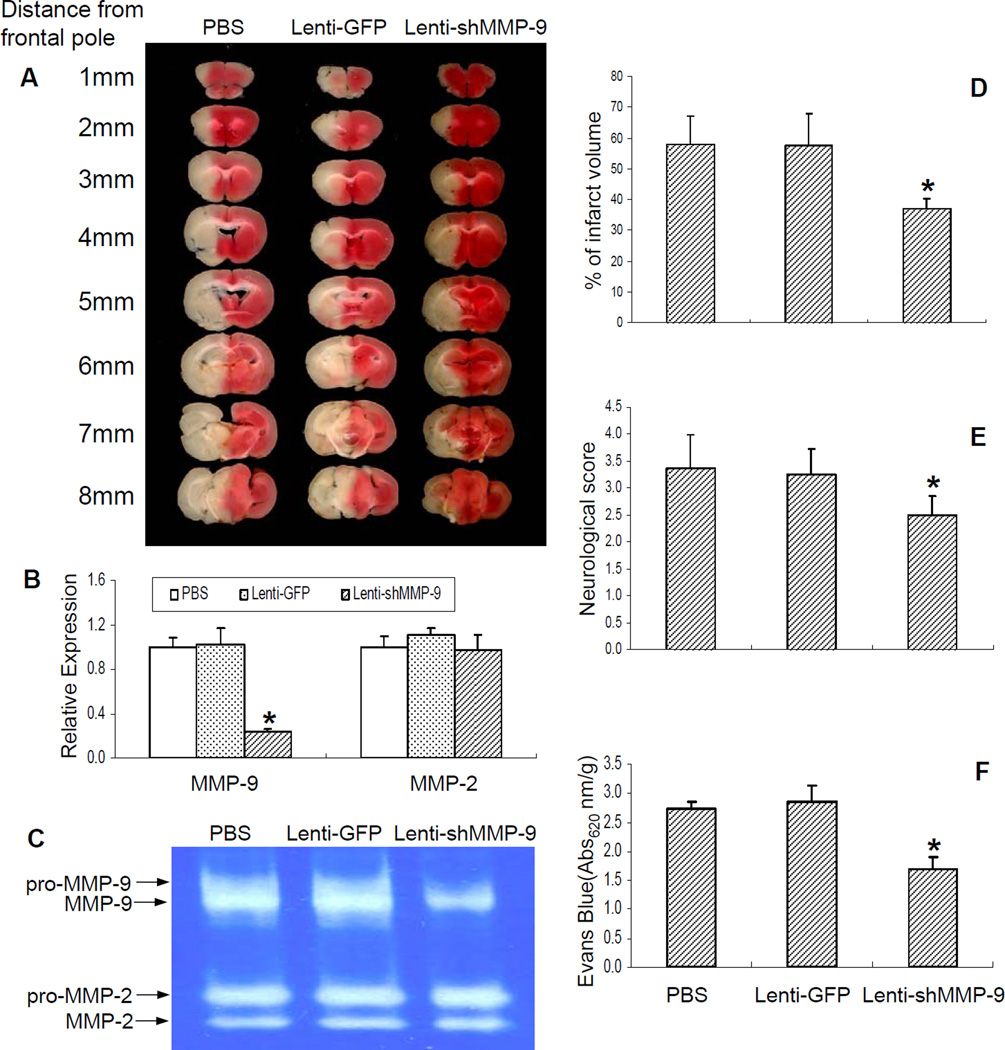
Figure 6.
The effect of lentivirus-mediated MMP-9 RNA interference on ischemia-induced brain infarction and cerebrovascular permeability. VSMC-selective PPARδ knockout (SMPδ cKO) mice were stereotactically injected 2 ul of a lentivirus carrying the shMMP-9 gene to ischemic regions and allowed to survive for 4 weeks. The mice were then subjected to MCAO and 24 h of reperfusion. 2% TTC-stained coronal sections were shown at different brain levels posterior to the frontal pole (A). Quantitative PCR and gelatin-based zymography were performed to measure MMP-2 and MMP-9 mRNA expression (B) and activities (C). Quantitative analysis was made on brain infarct volume (D) as well as neurological outcomes (E), and cerebrovascular permeability was determined 1 h after Evans Blue injection (F) in SMPδ cKO mice. In comparison with PBS or Lenti-GFP control groups, loss-of-MMP-9 function through lentivirus-mediated MMP-9 RNA interference significantly attenuates ischemic brain infarction (n=6–7) and improves neurological deficit (n=7–9) as well as cerebrovascular permeability (n=6). The effectiveness of this treatment was confirmed by a significant reduction of MMP-9 mRNA levels and activity. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. * p < 0.05 vs the PBS or Lenti-GFP group.