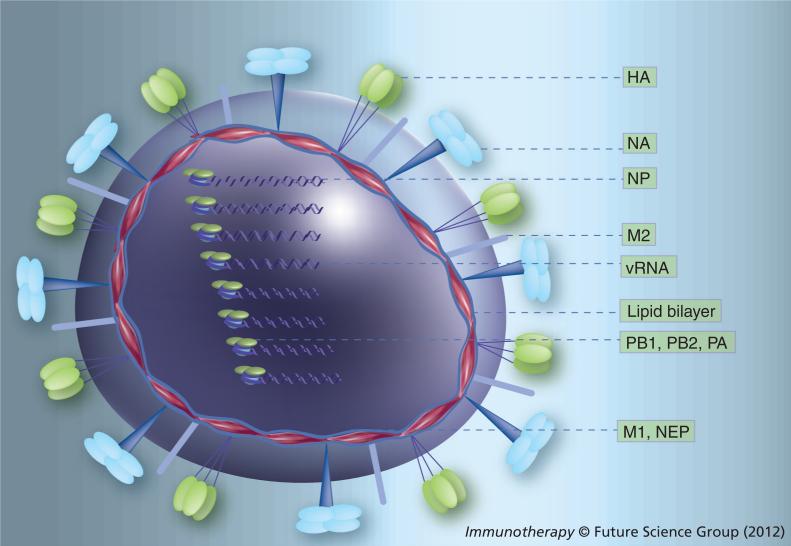
Figure 1. Molecular structure of influenza A viruses.
The virus contains a lipid bilayer derived from the host plasma membrane. Two surface glycoproteins, HA and NA, are the major antigenic determinants of the virus. The virus surface also carries a few copies of an ion channel proton pump (M2). Eight vRNA segments, each one of them associated to three polymerase subunits (PB2, PB1 and PA) and several copies of NP [6], are located inside the virion, protected by a protein mesh provided by the M. In addition, the virus carries a few copies of the virus-encoded NEP. In infected cells, the virus expresses NS1 and some influenza strains express PB1-F2, derived from the second open reading frame of segment 2.
HA: Hemagglutinin; M: Matrix protein; M2: Matrix protein 2; NA: Neuraminidase; NEP: Nuclear export protein; NP: Nucleoprotein; PA: Polymerase acidic protein; PB: Polymerase basic protein; vRNA: Viral RNA.