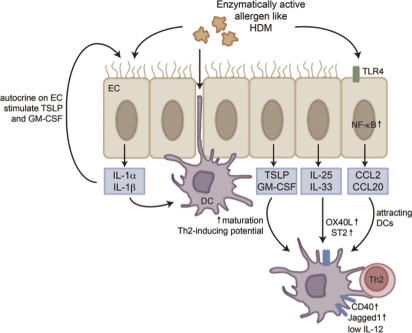
Figure 2. Interactions between airway epithelial cells and dendritic cells.
Dendritic cells (DCs) sample the airway lumen by forming dendritic extensions between epithelial cells. Enzymatically active allergens, like house dust mite can stimulate airway epithelial cells, via TLR(toll-like receptor)4 followed by NF-κB (nuclear factor-κB) activation, to produce chemokines and cytokines that attract and activate DCs. Certain cytokines, like IL(interleukin)-25 and IL-33 will lead to the upregulation of OX40L, CD40 and ST2, which will lead to polarization of CD4+ T cells towards a Th2 phenotype. Other cytokines like IL-1α and β activate DCs, but also have a positive autocrine feedback on epithelial cells and further stimulate the production of TSLP and GM-CSF. Abbreviations: DC, dendritic cell; EC, epithelial cell; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor; HDM, house dust mite; IL, interleukin; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; TLR, toll-like receptor; TSLP, thymic stromal lymphopoietin.