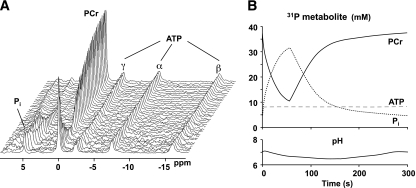
FIG. 4.
A: Dynamic 31P-MRS data acquired during muscle contraction and recovery (data courtesy of J. Kent-Braun). B: To maintain cellular ATP concentrations (dashed line) during the contraction, PCr (solid line) is depleted because of the CK reaction and Pi (dotted line) accumulates. Intracellular pH, calculated from the chemical shift separation between the PCr and Pi peaks, increases initially as a result of PCr hydrolysis; H+ production attributed to anaerobic glycolysis may cause intracellular acidification during longer contraction protocols. PCr, Pi, and pH recover to baseline upon cessation of the contraction.