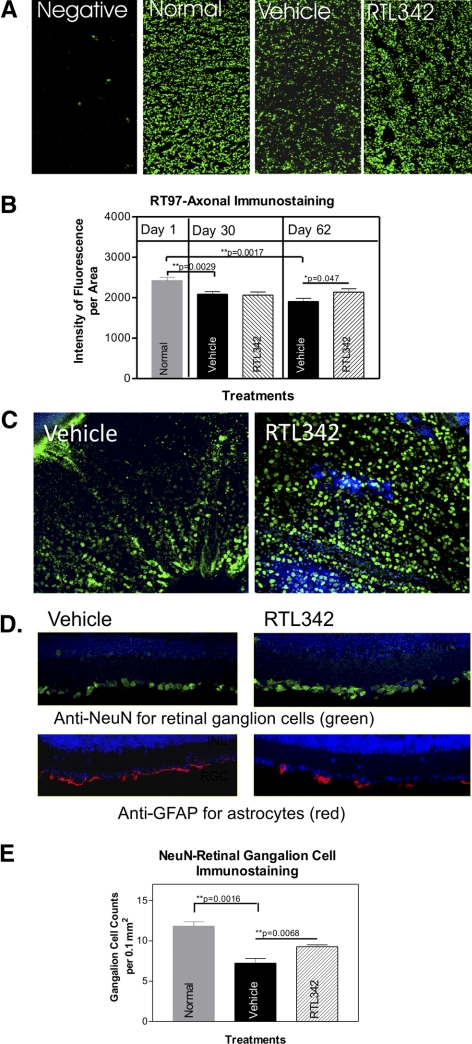
Figure 6.
Immunofluorescent labeling of surviving axons and RGCs in the optic nerve from vehicle- and RTL342M-treated mice collected on day 62 PI. (A) Immunostaining of cross sections with anti-RT97 antibodies for axons in normal and treatment groups collected on day 62 PI. Note a visible reduction in RT97-labeled axons in vehicle-treated optic nerves compared with normal and RTL342M-treated optic nerves; (B) quantitative analysis of fluorescence density of RT97 axonal labeling in vehicle- and RTL342M-treated optic nerves collected on days 30 and 62 PI. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM of fluorescence density in four sections 30 μm apart in stained optic nerves (n = 4). (C) Representative images of retinal whole mounts demonstrate NeuN-labeled RGCs on day 62 PI taken from RTL342M- and vehicle-treated mice. (D) Double-immunofluorescence labeling in the retina with anti-NeuN as a marker for RGCs and anti-GFAP antibodies as marker for astrocytes: anti-GFAP (red), anti-NeuN (green), nuclear labeling with DAPI (blue); the pictures show the ganglion cell layer of representative cross sections of eyes collected from vehicle- and RTL342M-treated mice. (E) Quantitative analysis of immunofluorescence-labeled RGCs with NeuN antibodies in retinal cross-sections in vehicle- and RTL342M-treated mice collected on day 62 PI. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM of fluorescent cell counts from four areas of the retina (n = 4) and normalized to a 0.1-mm2 area.