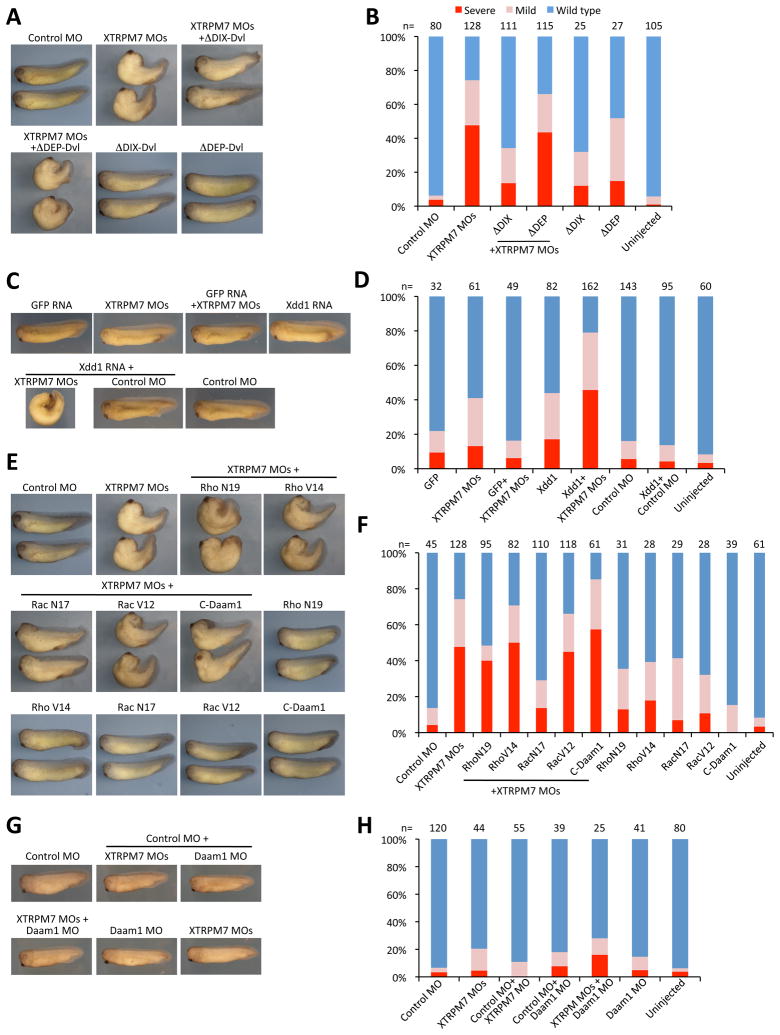
Fig. 5. TRPM7 is required for regulation of Rac and non-canonical Wnt signaling.
(A) Disruption of gastrulation produced by injection of XTRPM7 MOs (75 ng) can be suppressed by co-injection of dominant active Dishevelled (ΔDIX-Dvl) RNA (400 pg), but not by injection of Dishevelled lacking the DEP domain (ΔDEP-Dvl, 400 pg), whose deletion disrupts activation of the Rac component of the PCP pathway. (B) Quantification of the phenotypes observed with separate or co-injections of XTRPM7 MOs with ΔDIX-Dvl, and ΔDEP-Dvl RNAs. The number of embryos scored is indicated above each bar. (C) Co-injection of dominant negative Dishevelled (Xdd1) RNA (250 pg) and XTRPM7 MOs (25 ng) synergistically inhibit gastrulation but have little or no effect when injected separately. GFP RNA was injected at 250 pg. (D) Quantification of the phenotypes observed with separate or co-injections of XTRPM7 MOs with Xdd1. The number of embryos scored is indicated above each bar. (E) Co-injection of XTRPM7 MOs with dominant negative RacN17 RNA (500 pg), but not with C-Daam1 cDNA (250 pg), RNAs for dominant negative RhoN19 (500 pg) or with the dominant active mutants RacV12 (10 pg) and RhoV14 (10 pg), prevents the disruption of gastrulation caused by the XTRPM7 MOs. (F) Quantification of the phenotypes observed with separate or co-injections of XTRPM7 MOs with RacN17, RacV12, RhoN19 and RhoV14 RNAs and C-Daam1 cDNA. The number of embryos scored is indicated above each bar. (G) Co-injection of a low concentration of XTRPM7 MOs (25 ng) with control MO (25 ng) or with Daam1 MO (25 ng) did not produce synergistic gastrulation defects. (H) Quantification of the phenotypes observed with separate or co-injections of XTRPM7 MOs with control MO or Daam1 MO. The number of embryos scored is indicated above each bar.