Figure 4.
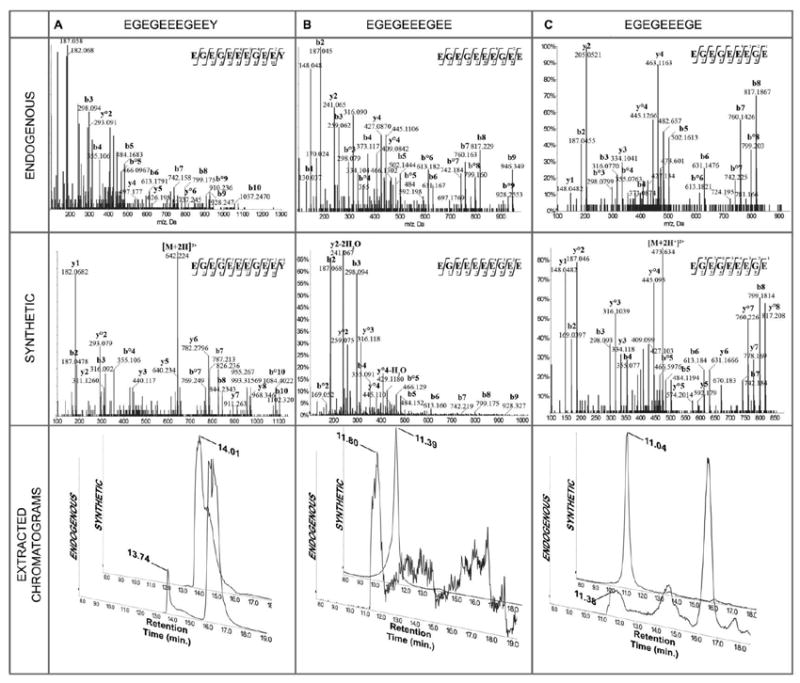
CID MS/MS of endogenous (top), synthetic (middle), and extracted chromatograms (bottom) of (A) tyrosinated tubulin-α1A/1B CTT: precursor ions were doubly charged at m/z 619.7040 for the synthetic peptide (tR 14.01 min.) with a neutral loss of H2O, and m/z 642.7346 for the endogenous one (tR 13.74 min.) with 2 methylations; extracted ions created by targeting these 2 ions showed close retention times; (B)detyrosinated tubulin-α1A/1B CTT: precursor ions were doubly charged at m/z 547.1812 for the synthetic peptide (tR 11.39 min.) with 2 neutral losses of H2O, and singly charged at m/z 1075.3301 for the endogenous one (tR 11.80 min.) with 2 neutral losses of H2O; extracted ions created by targeting these 2 ions showed close retention times; (C) Δ2-tubulin-α1A/1B CTT: precursor ions were doubly charged at m/z 482.6544 for the synthetic peptide (tR 11.04 min), and doubly charged at m/z 473.6524 for the endogenous one (tR 11.38 min.) with 1 neutral loss of H2O; extracted ions created by targeting these 2 ions showed close retention times. Fragmentation patterns of synthetic and endogenous peptides were similar after accounting for the methylation of endogenous peptides and the differential dehydration between endogenous and synthetic CTTs.
