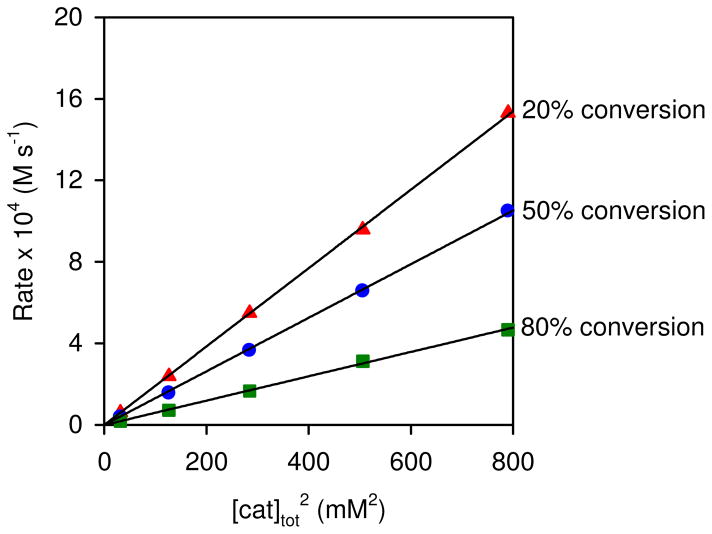
Figure 1.
Rate dependence of epoxide hydrolysis on [cat]tot 2 and %-conversion. Plots of the rate of hydrolysis of (R)-1,2-epoxyhexane ([epoxide]i = 5.63 M) versus [(S,S)-(salen)Co–OH]2 in 1,2-hexanediol ([diol]i = 2.18 M) at different %-conversion of water ([H2O]i = 2.82 M). The catalyst was generated by aging (S,S)-(salen)Co–Cl in epoxide for 1 h prior to addition of water. The black curves represent least-squares fits to f(x) = a x, 20 % conversion, a = 1.92 ± 0.01 M−1 s−1; 50 % conversion, a = 1.314 ± 0.009 M−1 s−1; 80 % conversion, a = 0.597 ± 0.006 M−1 s−1.